Autism spectrum: Difference between revisions
Autism diagnostic process because very long |
Rescuing orphaned refs ("Kanne 2008" from rev 1159500733; "Levy 2009" from rev 1159500733; "Mash & Barkley" from rev 1159500733) |
||
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
=== Biological subgroups === |
=== Biological subgroups === |
||
Research into causes has been hampered by the inability to identify biologically meaningful subgroups within the autistic population<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Altevogt BM, Hanson SL, Leshner AI |date=June 2008 |title=Autism and the environment: challenges and opportunities for research |url=http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/121/6/1225 |journal=Pediatrics |volume=121 |issue=6 |pages=1225–1229 |doi=10.1542/peds.2007-3000 |pmid=18519493 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100115140620/http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/121/6/1225 |archive-date=15 January 2010 |s2cid=24595814}}</ref> and by the traditional boundaries between the disciplines of [[psychiatry]], [[psychology]], [[neurology]] and [[pediatrics]].<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Reiss AL |date=January 2009 |title=Childhood developmental disorders: an academic and clinical convergence point for psychiatry, neurology, psychology and pediatrics |journal=Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines| issn = 0021-9630 | eissn = 1469-7610 | oclc = 01307942 |volume=50 |issue=1–2 |pages=87–98 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.02046.x |pmc=5756732 |pmid=19220592}}</ref> Newer technologies such as [[Functional magnetic resonance imaging|fMRI]] and [[diffusion tensor imaging]] can help identify biologically relevant [[phenotype]]s (observable traits) that can be viewed on [[Neuroimaging|brain scans]], to help further [[Neurogenetics|neurogenetic]] studies of autism;<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Piggot J, Shirinyan D, Shemmassian S, Vazirian S, Alarcón M |date=November 2009 |title=Neural systems approaches to the neurogenetics of autism spectrum disorders |journal=Neuroscience |volume=164 |issue=1 |pages=247–256 |doi=10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.054 |pmid=19482063 |s2cid=207246176}}</ref> one example is lowered activity in the [[fusiform face area]] of the brain, which is associated with impaired perception of people versus objects.<ref name="Levy 2009" /> It has been proposed to classify autism using genetics as well as behavior.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Stephan DA |date=January 2008 |title=Unraveling autism |journal=American Journal of Human Genetics |volume=82 |issue=1 |pages=7–9 |doi=10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.12.003 |pmc=2253980 |pmid=18179879}}</ref> (For more, see [[Brett Abrahams]]) |
Research into causes has been hampered by the inability to identify biologically meaningful subgroups within the autistic population<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Altevogt BM, Hanson SL, Leshner AI |date=June 2008 |title=Autism and the environment: challenges and opportunities for research |url=http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/121/6/1225 |journal=Pediatrics |volume=121 |issue=6 |pages=1225–1229 |doi=10.1542/peds.2007-3000 |pmid=18519493 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100115140620/http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/121/6/1225 |archive-date=15 January 2010 |s2cid=24595814}}</ref> and by the traditional boundaries between the disciplines of [[psychiatry]], [[psychology]], [[neurology]] and [[pediatrics]].<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Reiss AL |date=January 2009 |title=Childhood developmental disorders: an academic and clinical convergence point for psychiatry, neurology, psychology and pediatrics |journal=Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines| issn = 0021-9630 | eissn = 1469-7610 | oclc = 01307942 |volume=50 |issue=1–2 |pages=87–98 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.02046.x |pmc=5756732 |pmid=19220592}}</ref> Newer technologies such as [[Functional magnetic resonance imaging|fMRI]] and [[diffusion tensor imaging]] can help identify biologically relevant [[phenotype]]s (observable traits) that can be viewed on [[Neuroimaging|brain scans]], to help further [[Neurogenetics|neurogenetic]] studies of autism;<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Piggot J, Shirinyan D, Shemmassian S, Vazirian S, Alarcón M |date=November 2009 |title=Neural systems approaches to the neurogenetics of autism spectrum disorders |journal=Neuroscience |volume=164 |issue=1 |pages=247–256 |doi=10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.054 |pmid=19482063 |s2cid=207246176}}</ref> one example is lowered activity in the [[fusiform face area]] of the brain, which is associated with impaired perception of people versus objects.<ref name="Levy 2009">{{cite journal |vauthors=Levy SE, Mandell DS, Schultz RT |date=November 2009 |title=Autism |journal=Lancet |volume=374 |issue=9701 |pages=1627–1638 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61376-3 |pmc=2863325 |pmid=19819542}}{{Erratum|https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(11)61666-8/fulltext|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61666-8|checked=yes}}</ref> It has been proposed to classify autism using genetics as well as behavior.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Stephan DA |date=January 2008 |title=Unraveling autism |journal=American Journal of Human Genetics |volume=82 |issue=1 |pages=7–9 |doi=10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.12.003 |pmc=2253980 |pmid=18179879}}</ref> (For more, see [[Brett Abrahams]]) |
||
==== Syndromic autism and non-syndromic autism ==== |
==== Syndromic autism and non-syndromic autism ==== |
||
| Line 310: | Line 310: | ||
A 2018 Cochrane meta-analysis database concludes how some recent research is beginning to suggest that because of the heterology of ASD, there is two varying ABA teaching approaches to acquiring [[spoken language]]: children with more general [[expressive language disorder|expressive language delays]] respond sufficiently to the [[pivotal response treatment|naturalistic approach]], whereas children with [[mixed receptive-expressive language disorder|receptive language delays]] require [[discrete trial training]]—a structured and intensive form of ABA.<ref name="Cochrane">{{cite journal | vauthors = Brignell A, Chenausky KV, Song H, Zhu J, Suo C, Morgan AT | title = Communication interventions for autism spectrum disorder in minimally verbal children | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2018 | issue = 11 | pages = CD012324 | date = November 2018 | pmid = 30395694 | pmc = 6516977 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD012324.pub2 }}</ref> |
A 2018 Cochrane meta-analysis database concludes how some recent research is beginning to suggest that because of the heterology of ASD, there is two varying ABA teaching approaches to acquiring [[spoken language]]: children with more general [[expressive language disorder|expressive language delays]] respond sufficiently to the [[pivotal response treatment|naturalistic approach]], whereas children with [[mixed receptive-expressive language disorder|receptive language delays]] require [[discrete trial training]]—a structured and intensive form of ABA.<ref name="Cochrane">{{cite journal | vauthors = Brignell A, Chenausky KV, Song H, Zhu J, Suo C, Morgan AT | title = Communication interventions for autism spectrum disorder in minimally verbal children | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2018 | issue = 11 | pages = CD012324 | date = November 2018 | pmid = 30395694 | pmc = 6516977 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD012324.pub2 }}</ref> |
||
Similarly, a teacher-implemented intervention that utilizes a more [[Pivotal response treatment|naturalistic form of ABA]] combined with a developmental social pragmatic approach has been found to be beneficial in improving social-communication skills in young children, although there is less evidence in its treatment of global symptoms.<ref name=":06" /> Neuropsychological reports are often poorly communicated to educators, resulting in a gap between what a report recommends and what education is provided.<ref name="Kanne 2008" /> The appropriateness of including children with varying severity of autism spectrum disorders in the general education population is a subject of current debate among educators and researchers.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Simpson RL, de Boer-Ott SR, Smith-Myles B |year=2003 |title=Inclusion of Learners with Autism Spectrum Disorders in General Education Settings |url=http://www.nursingcenter.com/pdf.asp?AID=520301 |journal=Topics in Language Disorders |volume=23 |issue=2 |pages=116–133 |doi=10.1097/00011363-200304000-00005 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110714215923/http://www.nursingcenter.com/pdf.asp?AID=520301 |archive-date=14 July 2011 |s2cid=143733343}}</ref> |
Similarly, a teacher-implemented intervention that utilizes a more [[Pivotal response treatment|naturalistic form of ABA]] combined with a developmental social pragmatic approach has been found to be beneficial in improving social-communication skills in young children, although there is less evidence in its treatment of global symptoms.<ref name=":06" /> Neuropsychological reports are often poorly communicated to educators, resulting in a gap between what a report recommends and what education is provided.<ref name="Kanne 2008">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kanne SM, Randolph JK, Farmer JE |date=December 2008 |title=Diagnostic and assessment findings: a bridge to academic planning for children with autism spectrum disorders |journal=Neuropsychology Review |volume=18 |issue=4 |pages=367–384 |doi=10.1007/s11065-008-9072-z |pmid=18855144 |s2cid=21108225}}</ref> The appropriateness of including children with varying severity of autism spectrum disorders in the general education population is a subject of current debate among educators and researchers.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Simpson RL, de Boer-Ott SR, Smith-Myles B |year=2003 |title=Inclusion of Learners with Autism Spectrum Disorders in General Education Settings |url=http://www.nursingcenter.com/pdf.asp?AID=520301 |journal=Topics in Language Disorders |volume=23 |issue=2 |pages=116–133 |doi=10.1097/00011363-200304000-00005 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110714215923/http://www.nursingcenter.com/pdf.asp?AID=520301 |archive-date=14 July 2011 |s2cid=143733343}}</ref> |
||
===Pharmacological interventions=== |
===Pharmacological interventions=== |
||
| Line 353: | Line 353: | ||
====Differential outcomes ==== |
====Differential outcomes ==== |
||
There continues to be a debate over the differential outcomes based on these two developmental courses. Some studies suggest that regression is associated with poorer outcomes and others report no differences between those with early gradual onset and those who experience a regression period.<ref name="Mash & Barkley" /> While there is conflicting evidence surrounding language outcomes in autism, some studies have shown that cognitive and language abilities at age {{frac|2|1|2}} may help predict language proficiency and production after age 5.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Ellis Weismer S, Kover ST |date=December 2015 |title=Preschool language variation, growth, and predictors in children on the autism spectrum |journal=Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines |volume=56 |issue=12 |pages=1327–37 |doi=10.1111/jcpp.12406 |issn=0021-9630 |eissn=1469-7610 |oclc=01307942 |pmc=4565784 |pmid=25753577}}</ref> Overall, the literature stresses the importance of early intervention in achieving positive longitudinal outcomes.<ref name="Dawson & Osterling">{{cite book |title=The effectiveness of early intervention |vauthors=Dawson G, Osterling J |publisher=Brookes |year=1997 |isbn=1-55766-255-X |veditors=Guralnick MJ |location=Baltimore |pages=307–326 |chapter=Early Intervention in Autism |oclc=34411043 |id={{ERIC|ED414694}}}}</ref> |
There continues to be a debate over the differential outcomes based on these two developmental courses. Some studies suggest that regression is associated with poorer outcomes and others report no differences between those with early gradual onset and those who experience a regression period.<ref name="Mash & Barkley">{{cite book |url=https://archive.org/details/childpsychopatho00mash_735 |title=Child Psychopathology |vauthors=Mash EJ, Barkley RA |publisher=The Guilford Press |year=2003 |isbn=9781572306097 |location=New York |pages=[https://archive.org/details/childpsychopatho00mash_735/page/n421 409]–454 |url-access=limited}}</ref> While there is conflicting evidence surrounding language outcomes in autism, some studies have shown that cognitive and language abilities at age {{frac|2|1|2}} may help predict language proficiency and production after age 5.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Ellis Weismer S, Kover ST |date=December 2015 |title=Preschool language variation, growth, and predictors in children on the autism spectrum |journal=Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines |volume=56 |issue=12 |pages=1327–37 |doi=10.1111/jcpp.12406 |issn=0021-9630 |eissn=1469-7610 |oclc=01307942 |pmc=4565784 |pmid=25753577}}</ref> Overall, the literature stresses the importance of early intervention in achieving positive longitudinal outcomes.<ref name="Dawson & Osterling">{{cite book |title=The effectiveness of early intervention |vauthors=Dawson G, Osterling J |publisher=Brookes |year=1997 |isbn=1-55766-255-X |veditors=Guralnick MJ |location=Baltimore |pages=307–326 |chapter=Early Intervention in Autism |oclc=34411043 |id={{ERIC|ED414694}}}}</ref> |
||
===Academic performance=== |
===Academic performance=== |
||
Revision as of 19:06, 10 June 2023
This article may be too long to read and navigate comfortably. (June 2023) |
| Autism | |
|---|---|
| Other names |
|
 | |
| Repetitively stacking or lining up objects is a common trait associated with autism. | |
| Specialty | Psychiatry, clinical psychology, pediatrics, occupational medicine |
| Symptoms | Difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior or restricted interests |
| Complications | Social isolation, educational and employment problems,[1] anxiety,[1] stress,[1] bullying, depression,[2][1] self-harm |
| Onset | Early childhood |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Causes | Multifactorial, with many uncertain factors |
| Risk factors | Family history, certain genetic conditions, having older parents, certain prescribed drugs, perinatal and neonatal health issues |
| Diagnostic method | Based on combination of clinical observation of behavior and development and comprehensive diagnostic testing completed by a team of qualified professionals (including clinical psychologists, neuropsychologists, pediatricians, and speech-language pathologists) |
| Differential diagnosis | Intellectual disability, anxiety, bipolar disorder, depression, Rett syndrome, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, schizoid personality disorder, selective mutism, schizophrenia, obsessive–compulsive disorder, social anxiety disorder, Einstein syndrome, PTSD,[3] learning disorders (mainly speech disorders), social anxiety |
| Management | Applied behavior analysis, cognitive behavioral therapy, occupational therapy, psychotropic medication,[4] speech–language pathology |
| Frequency |
|
Autism, formally called autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by deficits in social communication and social interaction, and repetitive or restricted patterns of behaviors, interests, or activities, which can include hyper- and hyporeactivity to sensory input. Autism is a spectrum disorder, meaning that it can manifest very differently in each person. For example, some are nonspeaking, while others have proficient spoken language. Because of this, there is wide variation in the support needs of people across the autism spectrum.
Psychiatry has traditionally classified autism as a mental disorder, while the autism rights movement and a small but increasing number of researchers see autism as part of neurodiversity, the natural diversity in human thinking and experience, with strengths, differences, and weaknesses.[6] From this point of view, autistic people often still have a disability, but need to be accommodated, rather than cured.[7][8] This perspective has led to significant controversy among those who are autistic alongside advocates, practitioners, and charities.[9][10]
There are many theories about what causes autism; it is highly heritable and believed to be mainly genetic, but many genes are involved, and environmental factors may also be relevant.[11] The syndrome frequently co-occurs with other conditions, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, epilepsy, and intellectual disability. Disagreements continue about questions such as what should be included as part of the diagnosis, whether there are meaningful subtypes of autism,[12] and the significance of autism-associated traits in the wider population.[13][14] The combination of broader criteria and increased awareness has led to a trend of steadily increasing estimates of autism prevalence, causing a misconception that there is an autism epidemic[15] and perpetuating the myth that it is caused by vaccines.[16]
There is no known method to prevent or cure autism. Many forms of therapy, such as speech and occupational therapy, have been developed that may help autistic people. Some forms of therapy, such as applied behavior analysis, are controversial in the autism rights movement, with many advocates considering them unhelpful and unethical.[17] Intervention can require accommodations such as alternative modes of communication. The use of medicine is usually focused on associated conditions such as epilepsy or treating certain symptoms.[18]
Classification
Spectrum model
Before the DSM-5 (2013) and ICD-11 (2022) diagnostic manuals were adopted, what is now called ASD was found under the diagnostic category pervasive developmental disorder. The previous system relied on a set of closely related and overlapping diagnoses such as Asperger syndrome and Kanner syndrome. This created unclear boundaries between the terms, so for the DSM-5 and ICD-11, a spectrum approach was taken. The new system is also more restrictive, meaning fewer people now qualify for diagnosis.[19]
The DSM-5 and ICD-11 use different categorisation tools to define this spectrum. DSM-5 uses a "level" system, which ranks how in need of support the patient is,[20] while the ICD-11 system has two axes: intellectual impairment and language impairment,[21] as these are seen as the most crucial factors.
It is now known that autism is a highly variable neurodevelopmental disorder[22] that is generally thought to cover a broad and deep spectrum, manifesting very differently from one person to another. Some have high support needs, may be non-speaking, and experience developmental delays; this is more likely with other co-existing diagnoses. Others have relatively low support needs; they may have more typical speech-language and intellectual skills but atypical social/conversation skills, narrowly focused interests, and wordy, pedantic communication.[23] They may still require significant support in some areas of their lives. The spectrum model should not be understood as a continuum running from mild to severe, but instead means that autism can present very differently in each individual.[24] How a person presents can depend on context, and may vary over time.[25]
While the DSM and ICD are greatly influenced by each other, there are also differences. For example, Rett syndrome was included in ASD in the DSM-5, but in the ICD-11 it was excluded and placed in the chapter on Developmental Anomalies. The ICD and the DSM change over time, and there has been collaborative work toward a convergence of the two since 1980 (when DSM-III was published and ICD-9 was current), including more rigorous biological assessment—in place of historical experience—and a simplification of the classification system.[26][27][28][29]
ICD
The World Health Organization's International Classification of Diseases (11th Revision), ICD-11, was released in June 2018 and came into full effect as of January 2022.[30][26] It describes ASD as follows:[31]
Autism spectrum disorder is characterised by persistent deficits in the ability to initiate and to sustain reciprocal social interaction and social communication, and by a range of restricted, repetitive, and inflexible patterns of behaviour, interests or activities that are clearly atypical or excessive for the individual's age and sociocultural context. The onset of the disorder occurs during the developmental period, typically in early childhood, but symptoms may not become fully manifest until later, when social demands exceed limited capacities. Deficits are sufficiently severe to cause impairment in personal, family, social, educational, occupational or other important areas of functioning and are usually a pervasive feature of the individual's functioning observable in all settings, although they may vary according to social, educational, or other context. Individuals along the spectrum exhibit a full range of intellectual functioning and language abilities.
— ICD-11, chapter 6, section A02
ICD-11 was produced by professionals from 55 countries out of the 90 involved and is the most widely used reference worldwide.
DSM
The American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR), released in 2022, is the current version of the DSM. It is the predominant mental health diagnostic system used in the United States and Canada, and is often used in Anglophone countries.
Its fifth edition, DSM-5, released in May 2013, was the first to define ASD as a single diagnosis,[32] which is still the case in the DSM-5-TR.[33] ASD encompasses previous diagnoses, including Asperger syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, PDD-NOS, and the range of diagnoses that included the word autism.[34] Rather than distinguishing among these diagnoses, the DSM-5 and DSM-5-TR adopt a dimensional approach to diagnosing disorders that fall underneath the autism spectrum umbrella in one diagnostic category. Within this category, the DSM-5 and the DSM include a framework that differentiates each individual by dimensions of symptom severity, as well as by associated features (i.e., the presence of other disorders or factors that likely contribute to the symptoms, other neurodevelopmental or mental disorders, intellectual disability, or language impairment).[33] The symptom domains are social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors, with the option of a separate severity—the negative impact of the symptoms on the individual—being specified for each domain, rather than an overall severity.[35] Before the DSM-5, the DSM separated social deficits and communication deficits into two domains.[36] Further, the DSM-5 changed to an onset age in the early developmental period, with a note that symptoms may manifest later when social demands exceed capabilities, rather than the previous, more restricted three years of age.[37] These changes remain in the DSM-5-TR.[33]
Common characteristics
Pre-diagnosis
For many autistic people, characteristics first appear during infancy or childhood and follow a steady course without remission (different developmental timelines are described in more detail below).[38] Autistic people may be severely impaired in some respects but average, or even superior, in others.[39][40][41]
Clinicians consider assessment for ASD when a patient shows:
- regular difficulties in social interaction or communication
- restricted or repetitive behaviors (often called "stimming")
- resistance to changes or restricted interests
These features are typically assessed with the following, when appropriate:
- problems in obtaining or sustaining employment or education
- difficulties in initiating or sustaining social relationships
- connections with mental health or learning disability services
- a history of neurodevelopmental conditions (including learning disabilities and ADHD) or mental health conditions.[42][43]
There are many signs associated with autism; the presentation varies widely:[44][45]
Common signs for autistic spectrum disorder - avoidance of eye-contact
- little or no babbling as an infant
- not showing interest in indicated objects
- delayed language skills (e.g. having a smaller vocabulary than peers or difficulty expressing themselves in words)
- reduced interest in other children or caretakers, possibly with more interest in objects
- difficulty playing reciprocal games (e.g. peek-a-boo)
- hyper- or hypo-sensitivity to or unusual response to the smell, texture, sound, taste, or appearance of things
- resistance to changes in routine
- repetitive, limited, or otherwise unusual usage of toys (e.g. lining up toys)
- repetition of words or phrases (echolalia)
- repetitive motions or movements, including stimming
- self-harming
Broader autism phenotype
The broader autism phenotype (BAP) describes individuals who may not have ASD but do have autistic traits, such as avoiding eye contact and stimming.[46]
Social and communication skills
In social contexts, autistic people may respond and behave differently than people without ASD.[47]
Impairments in social skills present many challenges for autistic people. Deficits in social skills may lead to problems with friendships, romantic relationships, daily living, and vocational success.[48] One study that examined the outcomes of autistic adults found that, compared to the general population, autistic people were less likely to be married, but it is unclear whether this outcome was due to deficits in social skills, intellectual impairment, or another reason.[49] One factor is likely discrimination against autistic people, which is perpetuated by myths—for example, the myth that they have no empathy.[50][51][52]
Until 2013, deficits in social function and communication were considered two separate symptom domains of autism.[53] The current social communication domain criteria for autism diagnosis require individuals to have deficits across three social skills: social-emotional reciprocity, nonverbal communication, and developing and sustaining relationships.[33]
A range of social-emotional reciprocity difficulties (an individual's ability to naturally engage in social interactions) may be present. Autistic individuals may lack mutual sharing of interests; many autistic children prefer not to play or interact with others. They may lack awareness or understanding of other people's thoughts or feelings: a child may get too close to peers (entering their personal space) without noticing that this makes them uncomfortable. They may also engage in atypical behaviors to gain attention: a child may push a peer to gain attention before starting a conversation.[54]
Older autistic children and adults perform worse on tests of face and emotion recognition than non-autistic individuals, although this may be due to the prevalence of alexithymia in autistic people rather than autism itself.[55]
Autistic people experience deficits in their ability to develop, maintain, and understand relationships, as well as difficulties adjusting behavior to fit social contexts.[56] ASD presents with impairments in pragmatic communication skills, such as difficulty initiating a conversation or failure to consider the listener's interests to sustain a conversation.[54][verification needed] The ability to be focused exclusively on one topic in communication is known as monotropism, and can be compared to "tunnel vision". It is common for autistic people to communicate strong interest in a specific topic, speaking in lesson-like monologues about their passion instead of enabling reciprocal communication.[57] What may look like self-involvement or indifference to others stems from a struggle to recognize or remember that other people have their own personalities, perspectives, and interests.[58][59] Another difference in pragmatic communication skills is that autistic people may not recognize the need to control the volume of their voice in different social settings; for example, they may speak loudly in libraries or movie theaters.[60]
Autistic people display atypical nonverbal behaviors or have difficulties with nonverbal communication. They may make infrequent eye contact: an autistic person may not make eye contact when called by name, or may avoid eye contact with an observer. Aversion of gaze can also be seen in anxiety disorders, but poor eye contact in autistic children is not due to shyness or anxiety; rather, it is overall diminished in quantity. Autistic people may struggle with both production and understanding of facial expressions. They often do not know how to recognize emotions from others' facial expressions, or may not respond with appropriate facial expressions. They may have trouble recognizing subtle expressions of emotion and identifying what various emotions mean for the conversation.[61][57] A defining feature is that autistic people have social impairments and often lack intuitions about others that many people take for granted. Temple Grandin, an autistic woman involved in autism activism, described her inability to understand the social communication of neurotypicals, or people with typical neural development, as leaving her feeling "like an anthropologist on Mars".[62] They may also not pick up on body language or social cues such as eye contact and facial expressions if they provide more information than the person can process at that time. They struggle with understanding the context and subtext of conversational or printed situations, and have trouble forming resulting conclusions about the content. This also results in a lack of social awareness and atypical language expression.[58] How facial expressions differ between those on the autism spectrum and neurotypical individuals is not clear.[63] Further, at least half of autistic children have unusual prosody.[60]
Autistic people may also experience difficulties with verbal communication. Differences in communication may be present from the first year of life, and may include delayed onset of babbling, unusual gestures, diminished responsiveness, and vocal patterns that are not synchronized with the caregiver. In the second and third years, autistic children have less frequent and less diverse babbling, consonants, words, and word combinations; their gestures are less often integrated with words. Autistic children are less likely to make requests or share experiences, and are more likely to simply repeat others' words (echolalia).[64] Joint attention seems to be necessary for functional speech, and deficits in joint attention seem to distinguish autistic infants.[65] For example, they may look at a pointing hand instead of the object to which the hand is pointing,[66][64] and they consistently fail to point at objects in order to comment on or share an experience.[65] Autistic children may have difficulty with imaginative play and with developing symbols into language.[64] Some autistic linguistic behaviors include repetitive or rigid language, and restricted interests in conversation. For example, a child might repeat words or insist on always talking about the same subject.[54] Echolalia may also be present in autistic individuals, for example by responding to a question by repeating the inquiry instead of answering.[57] Language impairment is also common in autistic children, but is not part of a diagnosis.[54] Many autistic children develop language skills at an uneven pace where they easily acquire some aspects of communication, while never fully developing others,[57] such as in some cases of hyperlexia. In some cases, individuals remain completely nonverbal throughout their lives. The CDC estimated that around 40% of autistic children don't speak at all, although the accompanying levels of literacy and nonverbal communication skills vary.[67]
Restricted and repetitive behaviors

ASD includes a wide variety of characteristics. Some of these include behavioral characteristics which widely range from slow development of social and learning skills to difficulties creating connections with other people. Autistic individuals may experience these challenges with forming connections due to anxiety or depression, which they are more likely to experience, and as a result isolate themselves.[68][medical citation needed]
Other behavioral characteristics include abnormal responses to sensations (such as sights, sounds, touch, taste and smell) and problems keeping a consistent speech rhythm. The latter problem influences an individual's social skills, leading to potential problems in how they are understood by communication partners. Behavioral characteristics displayed by autistic people typically influence development, language, and social competence. Behavioral characteristics of autistic people can be observed as perceptual disturbances, disturbances of development rate, relating, speech and language, and motility.[69]
The second core symptom of autism spectrum is a pattern of restricted and repetitive behaviors, activities, and interests. In order to be diagnosed with ASD under the DSM-5-TR, a person must have at least two of the following behaviors:[33][70]
- Repetitive behaviors – Repetitive behaviors such as rocking, hand flapping, finger flicking, head banging, or repeating phrases or sounds.[54] These behaviors may occur constantly or only when the person gets stressed, anxious or upset. These behaviors are also known as stimming.
- Resistance to change – A strict adherence to routines such as eating certain foods in a specific order, or taking the same path to school every day.[54] The individual may become distressed if there is any change or disruption to their routine.
- Restricted interests – An excessive interest in a particular activity, topic, or hobby, and devoting all their attention to it. For example, young children might completely focus on things that spin and ignore everything else. Older children might try to learn everything about a single topic, such as the weather or sports, and perseverate or talk about it constantly.[54]
- Sensory reactivity – An unusual reaction to certain sensory inputs such as having a negative reaction to specific sounds or textures, being fascinated by lights or movements or having an apparent indifference to pain or heat.[71]
Autistic individuals can display many forms of repetitive or restricted behavior, which the Repetitive Behavior Scale-Revised (RBS-R) categorizes as follows.[72]
- Stereotyped behaviors: Repetitive movements, such as hand flapping, head rolling, or body rocking.
- Compulsive behaviors: Time-consuming behaviors intended to reduce anxiety, that an individual feels compelled to perform repeatedly or according to rigid rules, such as placing objects in a specific order, checking things, or handwashing.
- Sameness: Resistance to change; for example, insisting that the furniture not be moved or refusing to be interrupted.
- Ritualistic behavior: Unvarying pattern of daily activities, such as an unchanging menu or a dressing ritual. This is closely associated with sameness and an independent validation has suggested combining the two factors.[72]
- Restricted interests: Interests or fixations that are abnormal in theme or intensity of focus, such as preoccupation with a single television program, toy, or game.
- Self-injury: Behaviors such as eye-poking, skin-picking, hand-biting and head-banging.[65]
Self-injury
Self-injurious behaviors (SIB) are relatively common in autistic people, and can include head-banging, self-cutting, self-biting, and hair-pulling.[73] Some of these behaviors can result in serious injury or death.[73] Following are theories about the cause of self-injurious behavior in children with developmental delay, including autistic individuals:[74]
- Frequency and/or continuation of self-injurious behavior can be influenced by environmental factors (e.g. reward in return for halting self-injurious behavior). However this theory is not applicable to younger children with autism. There is some evidence that frequency of self-injurious behavior can be reduced by removing or modifying environmental factors that reinforce this behavior.[74]: 10–12
- Higher rates of self-injury are also noted in socially isolated individuals with autism. Studies have shown that socialization skills are related factors to self injurious behavior for individuals with autism.[75]
- Self-injury could be a response to modulate pain perception when chronic pain or other health problems that cause pain are present.[74]: 12–13
- An abnormal basal ganglia connectivity may predispose to self-injurious behavior.[74]: 13
Other features
Autistic individuals may have symptoms that do not contribute to the official diagnosis, but that can affect the individual or the family.[76]
- Some individuals with ASD show unusual or notable abilities, ranging from splinter skills (such as the memorization of trivia) to rare talents in mathematics, music or artistic reproduction, which in exceptional cases are considered a part of the savant syndrome.[77][78][79] One study describes how some individuals with ASD show superior skills in perception and attention, relative to the general population.[80] Sensory abnormalities are found in over 90% of autistic people, and are considered core features by some.[81]
- More generally, autistic people tend to show a 'spiky skills profile', with strong abilities in some areas contrasting with much weaker abilities in others.[82]
- Differences between the previously recognized disorders under the autism spectrum are greater for under-responsivity (for example, walking into things) than for over-responsivity (for example, distress from loud noises) or for sensation seeking (for example, rhythmic movements).[83] An estimated 60–80% of autistic people have motor signs that include poor muscle tone, poor motor planning, and toe walking;[81][84] deficits in motor coordination are pervasive across ASD and are greater in autism proper.[85][86]
- Pathological demand avoidance can occur. People with this set of autistic symptoms are more likely to refuse to do what is asked or expected of them, even to activities they enjoy.
- Unusual or atypical eating behavior occurs in about three-quarters of children with ASD, to the extent that it was formerly a diagnostic indicator.[76] Selectivity is the most common problem, although eating rituals and food refusal also occur.[87]
- There is tentative evidence that gender dysphoria occurs more frequently in autistic people (see Autism and LGBT identities).[88][89] As well as that, a 2021 anonymized online survey of 16–90 year-olds revealed that autistic males are more likely to identify as bisexual, while autistic females are more likely to identify as homosexual.[90]
Possible causes
Exactly what causes autism remains unknown.[91][92][93][94] It was long mostly presumed that there is a common cause at the genetic, cognitive, and neural levels for the social and non-social components of ASD's symptoms, described as a triad in the classic autism criteria.[95] But it is increasingly suspected that autism is instead a complex disorder whose core aspects have distinct causes that often cooccur.[95][96] While it is unlikely that ASD has a single cause,[96] many risk factors identified in the research literature may contribute to ASD development. These include genetics, prenatal and perinatal factors (meaning factors during pregnancy or very early infancy), neuroanatomical abnormalities, and environmental factors. It is possible to identify general factors, but much more difficult to pinpoint specific ones. Given the current state of knowledge, prediction can only be of a global nature and therefore requires the use of general markers.[97]
Biological subgroups
Research into causes has been hampered by the inability to identify biologically meaningful subgroups within the autistic population[98] and by the traditional boundaries between the disciplines of psychiatry, psychology, neurology and pediatrics.[99] Newer technologies such as fMRI and diffusion tensor imaging can help identify biologically relevant phenotypes (observable traits) that can be viewed on brain scans, to help further neurogenetic studies of autism;[100] one example is lowered activity in the fusiform face area of the brain, which is associated with impaired perception of people versus objects.[101] It has been proposed to classify autism using genetics as well as behavior.[102] (For more, see Brett Abrahams)
Syndromic autism and non-syndromic autism
Autism spectrum disorder can be classified in two categories: "syndromic autism" and "non-syndromic autism". ASD is syndromic when it is one of the many characteristics that are associated with a more broad medical condition, generally a syndrome. Syndromic autism represents about 25% of the total ASD cases[103] and its etiology in most cases is known. Monogenic disorders are one of the causes of syndromic autism (in this case also known as "monogenic ASD"), they account for about 5% of the total ASD cases. Non-syndromic autism, also called "classic autism" and "idiopathic autism" (because in most cases etiology is unknown), represents the majority of total autism cases and in most cases its cause is polygenic. Certain syndromic form of ASD can also have different phenomenology. Studying the differences and similarities (e.g. common pathways) between syndromic and non-syndromic autism can also give more insight about its pathophysiology and pave the way to new treatments.[104][105][106][107]
A 2017 study, also proposed to replace the classification "syndromic"/"non-syndromic" ASD into a one based on the genetic etiology of the condition, specifying if the syndromic condition occurs in the context of a "phenotype first" clinically defined syndrome or from a "genotype first" molecularly defined syndrome. In this case ASD would be divided into three genetic categories:
- "Clinically defined": syndromes recognized by clinicians (depending on their experience), typically confirmed by a targeted genetic testing
- Chromosomal (e.g.: Down syndrome)
- Syndromes caused by mutations in single genes (e.g.: NF1, TSC, PTEN-associated macrocephaly syndrome, some males with FXS)
- Syndromes caused by CNVs (e.g.: microdeletion 22q11.2 syndrome)
- Teratogens (e.g: valproate aembryopathy)
- "Molecularly defined": syndromes recognized by genome-wide testing, not by hypothesis-driven testing (since clinical recognition is difficult)
- "Currently undefined"[107]
Genetics
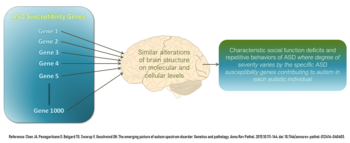
Autism has a strong genetic basis, although the genetics of autism are complex and it is unclear whether ASD is explained more by rare mutations with major effects, or by rare multi-gene interactions of common genetic variants.[109][110] Complexity arises due to interactions among multiple genes, the environment, and epigenetic factors which do not change DNA sequencing but are heritable and influence gene expression.[111] Many genes have been associated with autism through sequencing the genomes of affected individuals and their parents.[112] However, most of the mutations that increase autism risk have not been identified. Typically, autism cannot be traced to a Mendelian (single-gene) mutation or to a single chromosome abnormality, and none of the genetic syndromes associated with ASD have been shown to selectively cause ASD.[109] Numerous candidate genes have been located, with only small effects attributable to any particular gene.[109] Most loci individually explain less than 1% of cases of autism.[113] As of 2018[update], it appeared that between 74% and 93% of ASD risk is heritable.[70] After an older child is diagnosed with ASD, 7% to 20% of subsequent children are likely to be as well.[70] If parents have one autistic child, they have a 2% to 8% chance of having a second child who is autistic. If the autistic child is an identical twin, the other will be affected 36% to 95% of the time. A fraternal twin is affected up to 31% of the time.[medical citation needed] The large number of autistic people with unaffected family members may result from spontaneous structural variation, such as deletions, duplications or inversions in genetic material during meiosis.[114][115] Hence, a substantial fraction of autism cases may be traceable to genetic causes that are highly heritable but not inherited: that is, the mutation that causes the autism is not present in the parental genome.[116][verification needed]
As of 2018[update], understanding of genetic risk factors had shifted from a focus on a few alleles to an understanding that genetic involvement in ASD is probably diffuse, depending on a large number of variants, some of which are common and have a small effect, and some of which are rare and have a large effect. The most common gene disrupted with large effect rare variants appeared to be CHD8, but less than 0.5% of autistic people have such a mutation. The gene CHD8 encodes the protein chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 8, which is a chromatin regulator enzyme that is essential during fetal development, CHD8 is an ATP dependent enzyme.[117][118][119] The protein contains an Snf2 helicase domain that is responsible for the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP.[119] CHD8 encodes for a DNA helicase that function as a transcription repressor by remodeling chromatin structure by altering the position of nucleosomes. CHD8 negatively regulates Wnt signaling. Wnt signaling is important in the vertebrate early development and morphogenesis. It is believed that CHD8 also recruits the linker histone H1 and causes the repression of β-catenin and p53 target genes.[117] The importance of CHD8 can be observed in studies where CHD8-knockout mice died after 5.5 embryonic days because of widespread p53 induced apoptosis. Some studies have determined the role of CHD8 in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). CHD8 expression significantly increases during human mid-fetal development.[117] The chromatin remodeling activity and its interaction with transcriptional regulators have shown to play an important role in ASD aetiology.[118] The developing mammalian brain has a conserved CHD8 target regions that are associated with ASD risk genes.[120] The knockdown of CHD8 in human neural stem cells results in dysregulation of ASD risk genes that are targeted by CHD8.[121] Recently CD8 has been associated to the regulation of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs),[122] and the regulation of X chromosome inactivation (XCI) initiation, via regulation of Xist long non-coding RNA,[ambiguous] the master regulator of XCI,[ambiguous] though competitive binding to Xist regulatory regions.[123]
Some ASD is associated with clearly genetic conditions, like fragile X syndrome; however, only around 2% of autistic people have fragile X.[70] Hypotheses from evolutionary psychiatry suggest that these genes persist because they are linked to human inventiveness, intelligence or systemising.[124][125]
Current research suggests that genes that increase susceptibility to ASD are ones that control protein synthesis in neuronal cells in response to cell needs, activity and adhesion of neuronal cells, synapse formation and remodeling, and excitatory to inhibitory neurotransmitter balance. Therefore, despite up to 1000 different genes thought to contribute to increased risk of ASD, all of them eventually affect normal neural development and connectivity between different functional areas of the brain in a similar manner that is characteristic of an ASD brain. Some of these genes are known to modulate production of the GABA neurotransmitter which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the nervous system. These GABA-related genes are under-expressed in an ASD brain. On the other hand, genes controlling expression of glial and immune cells in the brain e.g. astrocytes and microglia, respectively, are over-expressed which correlates with increased number of glial and immune cells found in postmortem ASD brains. Some genes under investigation in ASD pathophysiology are those that affect the mTOR signaling pathway which supports cell growth and survival.[126]
All these genetic variants contribute to the development of the autistic spectrum; however, it cannot be guaranteed that they are determinants for the development.[127]
ASD may be under-diagnosed in women and girls due to an assumption that it is primarily a male condition,[128] but genetic phenomena such as imprinting and X linkage have the ability to raise the frequency and severity of conditions in males, and theories have been put forward for a genetic reason why males are diagnosed more often, such as the imprinted brain hypothesis and the extreme male brain theory.[129][130][131]
Early life
Several prenatal and perinatal complications have been reported as possible risk factors for autism. These risk factors include maternal gestational diabetes, maternal and paternal age over 30, bleeding during pregnancy after the first trimester, use of certain prescription medication (e.g. valproate) during pregnancy, and meconium in the amniotic fluid. While research is not conclusive on the relation of these factors to autism, each of these factors has been identified more frequently in children with autism, compared to their siblings who do not have autism, and other typically developing youth.[132] While it is unclear if any single factors during the prenatal phase affect the risk of autism,[133] complications during pregnancy may be a risk.[133]
There are also studies being done to test if certain types of regressive autism have an autoimmune basis.[134]
Maternal nutrition and inflammation during preconception and pregnancy influences fetal neurodevelopment. Intrauterine growth restriction is associated with ASD, in both term and preterm infants.[135] Maternal inflammatory and autoimmune diseases may damage fetal tissues, aggravating a genetic problem or damaging the nervous system.[136]
Exposure to air pollution during child pregnancy, especially heavy metals and particulates, may increase the risk of autism.[137][138] Environmental factors that have been claimed without evidence to contribute to or exacerbate autism include certain foods, infectious diseases, solvents, PCBs, phthalates and phenols used in plastic products, pesticides, brominated flame retardants, alcohol, smoking, illicit drugs, vaccines,[139] and prenatal stress. Some, such as the MMR vaccine, have been completely disproven.[140][141][142][143]
Disproven vaccine hypothesis
Parents may first become aware of ASD symptoms in their child around the time of a routine vaccination. This has led to unsupported and disproven theories blaming vaccine "overload", a vaccine preservative, or the MMR vaccine for causing autism spectrum disorder.[144] In 1998, British physician and academic Andrew Wakefield led a fraudulent, litigation-funded study that suggested that the MMR vaccine may cause autism.[145][146][147][148][149] This conjecture suggested that autism results from brain damage caused either by the MMR vaccine itself, or by thimerosal, a vaccine preservative.[150] No convincing scientific evidence supports these claims.[16] They are biologically implausible,[144] and further evidence continues to refute them, including the observation that the rate of autism continues to climb despite elimination of thimerosal from routine childhood vaccines.[151] A 2014 meta-analysis examined ten major studies on autism and vaccines involving 1.25 million children worldwide; it concluded that neither the MMR vaccine, which has never contained thimerosal,[152] nor the vaccine components thimerosal or mercury, lead to the development of ASDs.[153] Despite this, misplaced parental concern has led to lower rates of childhood immunizations, outbreaks of previously controlled childhood diseases in some countries, and the preventable deaths of several children.[154][155]
Etiological hypotheses
Several hypotheses have been presented that try to explain how and why autism develops by integrating known causes (genetic and environmental effects) and findings (neurobiological and somatic). Some are more comprehensive, such as the Pathogenetic Triad,[156] which proposes and operationalizes three core features (an autistic personality, cognitive compensation, neuropathological burden) that interact to cause autism, and the Intense World Theory,[157] which explains autism through a hyper-active neurobiology that leads to an increased perception, attention, memory, and emotionality. There are also simpler hypotheses that explain only individual parts of the neurobiology or phenotype of autism, such as mind-blindness (a decreased ability for theory of mind), the weak central coherence theory, or the extreme male brain and empathising–systemising theory.
Evolutionary hypotheses
Research exploring the evolutionary benefits of autism and associated genes has suggested that autistic people may have played a "unique role in technological spheres and understanding of natural systems" in the course of human development.[158][159] It has been suggested that it may have arisen as "a slight trade off for other traits that are seen as highly advantageous", providing "advantages in tool making and mechanical thinking", with speculation that the condition may "reveal itself to be the result of a balanced polymorphism, like sickle cell anemia, that is advantageous in a certain mixture of genes and disadvantageous in specific combinations".[160]
In 2011, a paper in Evolutionary Psychology proposed that autistic traits, including increased abilities for spatial intelligence, concentration and memory, could have been naturally selected to enable self-sufficient foraging in a more (although not completely) solitary environment, referred to as the "Solitary Forager Hypothesis".[161][162][163] A 2016 paper examines Asperger syndrome as "an alternative prosocial adaptive strategy" which may have developed as a result of the emergence of "collaborative morality" in the context of small-scale hunter-gathering, i.e. where "a positive social reputation for making a contribution to group wellbeing and survival" becomes more important than complex social understanding.[164]
Conversely, some multidisciplinary research suggests that recent human evolution may be a driving force in the rise of a number of medical conditions in recent human populations, including autism. Studies in evolutionary medicine indicate that as biological evolution becomes outpaced by cultural evolution, disorders linked to bodily dysfunction increase in prevalence due to a lack of contact with pathogens and negative environmental conditions that once widely affected ancestral populations. Because natural selection primarily favors reproduction over health and longevity, the lack of this impetus to adapt to certain harmful circumstances creates a tendency for genes in descendant populations to over-express themselves, which may cause a wide array of maladies, ranging from mental disorders to autoimmune diseases.[165]
Pathophysiology
Autism's symptoms result from maturation-related changes in various systems of the brain.[166] How autism occurs is not yet well understood. Its mechanism can be divided into two areas: the pathophysiology of brain structures and processes associated with autism, and the neuropsychological linkages between brain structures and behaviors.[166] The behaviors appear to have multiple pathophysiologies.[167]
There is evidence that gut–brain axis abnormalities may be involved.[168][169][170] A 2015 review proposed that immune, gastrointestinal inflammation, malfunction of the autonomic nervous system, gut flora alterations, and food metabolites may cause brain neuroinflammation and dysfunction.[169] A 2016 review concludes that enteric nervous system abnormalities might play a role in neurological disorders such as autism. Neural connections and the immune system are a pathway that may allow diseases originated in the intestine spread to the brain.[170]
Several lines of evidence point to synaptic dysfunction as a cause of autism.[101] Some rare mutations may lead to autism by disrupting some synaptic pathways, such as those involved with cell adhesion.[171] All known teratogens (agents that cause birth defects) related to the risk of autism appear to act during the first eight weeks from conception, and though this does not exclude the possibility that autism can be initiated or affected later, there is strong evidence that autism arises very early in development.[172]
In general, neuroanatomical studies support the concept that autism may involve a combination of brain enlargement in some areas and reduction in others.[173] These studies suggest that autism may be caused by abnormal neuronal growth and pruning during the early stages of prenatal and postnatal brain development, leaving some areas of the brain with too many neurons and other areas with too few neurons.[174] Some research has reported an overall brain enlargement in autism, while others suggest abnormalities in several areas of the brain, including the frontal lobe, the mirror neuron system, the limbic system, the temporal lobe, and the corpus callosum.[175][176]
In functional neuroimaging studies, when performing theory of mind and facial emotion response tasks, the median person on the autism spectrum exhibits less activation in the primary and secondary somatosensory cortices of the brain than the median member of a properly sampled control population. This finding coincides with reports demonstrating abnormal patterns of cortical thickness and grey matter volume in those regions of autistic peoples' brains.[177]
Brain connectivity
Brains of autistic individuals have been observed to have abnormal connectivity and the degree of these abnormalities directly correlates with the severity of autism. Following are some observed abnormal connectivity patterns in autistic individuals:[178][126]
- Decreased connectivity between different specialized regions of the brain (e.g. lower neuron density in corpus callosum) and relative over-connectivity within specialized regions of the brain by adulthood. Connectivity between different regions of the brain ('long-range' connectivity) is important for integration and global processing of information and comparing incoming sensory information with the existing model of the world within the brain. Connections within each specialized regions ('short-range' connections) are important for processing individual details and modifying the existing model of the world within the brain to more closely reflect incoming sensory information. In infancy, children at high risk for autism that were later diagnosed with autism were observed to have abnormally high long-range connectivity which then decreased through childhood to eventual long-range under-connectivity by adulthood.[178]
- Abnormal preferential processing of information by the left hemisphere of the brain vs. preferential processing of information by right hemisphere in neurotypical individuals. The left hemisphere is associated with processing information related to details whereas the right hemisphere is associated with processing information in a more global and integrated sense that is essential for pattern recognition. For example, visual information like face recognition is normally processed by the right hemisphere which tends to integrate all information from an incoming sensory signal, whereas an ASD brain preferentially processes visual information in the left hemisphere where information tends to be processed for local details of the face rather than the overall configuration of the face. This left lateralization negatively impacts both facial recognition and spatial skills.[178]
- Increased functional connectivity within the left hemisphere which directly correlates with severity of autism. This observation also supports preferential processing of details of individual components of sensory information over global processing of sensory information in an ASD brain.[178]
- Prominent abnormal connectivity in the frontal and occipital regions. In autistic individuals low connectivity in the frontal cortex was observed from infancy through adulthood. This is in contrast to long-range connectivity which is high in infancy and low in adulthood in ASD.[178] Abnormal neural organization is also observed in the Broca's area which is important for speech production.[126]
Neuropathology
Listed below are some characteristic findings in ASD brains on molecular and cellular levels regardless of the specific genetic variation or mutation contributing to autism in a particular individual:
- Limbic system with smaller neurons that are more densely packed together. Given that the limbic system is the main center of emotions and memory in the human brain, this observation may explain social impairment in ASD.[126]
- Fewer and smaller Purkinje neurons in the cerebellum. New research suggest a role of the cerebellum in emotional processing and language.[126]
- Increased number of astrocytes and microglia in the cerebral cortex. These cells provide metabolic and functional support to neurons and act as immune cells in the nervous system, respectively.[126]
- Increased brain size in early childhood causing macrocephaly in 15–20% of ASD individuals. The brain size however normalizes by mid-childhood. This variation in brain size in not uniform in the ASD brain with some parts like the frontal and temporal lobes being larger, some like the parietal and occipital lobes being normal sized, and some like cerebellar vermis, corpus callosum, and basal ganglia being smaller than neurotypical individuals.[126]
- Cell adhesion molecules that are essential to formation and maintenance of connections between neurons, neuroligins found on postsynaptic neurons that bind presynaptic cell adhesion molecules, and proteins that anchor cell adhesion molecules to neurons are all found to be mutated in ASD.[126]
Gut-immune-brain axis
46% to 84% of autistic individuals have GI-related problems like reflux, diarrhea, constipation, inflammatory bowel disease, and food allergies.[179] It has been observed that the makeup of gut bacteria in autistic people is different than that of neurotypical individuals which has raised the question of influence of gut bacteria on ASD development via inducing an inflammatory state.[180] Listed below are some research findings on the influence of gut bacteria and abnormal immune responses on brain development:[180]
- Some studies on rodents have shown gut bacteria influencing emotional functions and neurotransmitter balance in the brain, both of which are impacted in ASD.[126]
- The immune system is thought to be the intermediary that modulates the influence of gut bacteria on the brain. Some ASD individuals have a dysfunctional immune system with higher numbers of some types of immune cells, biochemical messengers and modulators, and autoimmune antibodies. Increased inflammatory biomarkers correlate with increased severity of ASD symptoms and there is some evidence to support a state of chronic brain inflammation in ASD.[180]
- More pronounced inflammatory responses to bacteria were found in ASD individuals with an abnormal gut microbiota. Additionally, immunoglobulin A antibodies that are central to gut immunity were also found in elevated levels in ASD populations. Some of these antibodies may attack proteins that support myelination of the brain, a process that is important for robust transmission of neural signal in many nerves.[180]
- Activation of the maternal immune system during pregnancy (by gut bacteria, bacterial toxins, an infection, or non-infectious causes) and gut bacteria in the mother that induce increased levels of Th17, a pro-inflammatory immune cell, have been associated with an increased risk of autism. Some maternal IgG antibodies that cross the placenta to provide passive immunity to the fetus can also attack the fetal brain.[180]
- It is proposed that inflammation within the brain promoted by inflammatory responses to harmful gut microbiome impacts brain development.[180]
- Pro-inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ, IFN-α, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-17 have been shown to promote autistic behaviors in animal models. Giving anti-IL-6 and anti-IL-17 along with IL-6 and IL-17, respectively, have been shown to negate this effect in the same animal models.[180]
- Some gut proteins and microbial products can cross the blood–brain barrier and activate mast cells in the brain. Mast cells release pro-inflammatory factors and histamine which further increase blood–brain barrier permeability and help set up a cycle of chronic inflammation.[180]
Social brain interconnectivity
A number of discrete brain regions and networks among regions that are involved in dealing with other people have been discussed together under the rubric of the social brain. As of 2012[update], there is a consensus that autism spectrum is likely related to problems with interconnectivity among these regions and networks, rather than problems with any specific region or network.[181]
Temporal lobe
Functions of the temporal lobe are related to many of the deficits observed in individuals with ASDs, such as receptive language, social cognition, joint attention, action observation, and empathy. The temporal lobe also contains the superior temporal sulcus and the fusiform face area, which may mediate facial processing. It has been argued that dysfunction in the superior temporal sulcus underlies the social deficits that characterize autism. Compared to neurotypical individuals, one study found that individuals with high-functioning autism had reduced activity in the fusiform face area when viewing pictures of faces.[182][verification needed]
Mitochondria
ASD could be linked to mitochondrial disease, a basic cellular abnormality with the potential to cause disturbances in a wide range of body systems.[183] A 2012 meta-analysis study, as well as other population studies show that approximately 5% of autistic children meet the criteria for classical mitochondrial dysfunction.[184] It is unclear why this mitochondrial disease occurs, considering that only 23% of children with both ASD and mitochondrial disease present with mitochondrial DNA abnormalities.[184]
Serotonin
Serotonin is a major neurotransmitter in the nervous system and contributes to formation of new neurons (neurogenesis), formation of new connections between neurons (synaptogenesis), remodeling of synapses, and survival and migration of neurons, processes that are necessary for a developing brain and some also necessary for learning in the adult brain. 45% of ASD individuals have been found to have increased blood serotonin levels.[126] It has been hypothesized that increased activity of serotonin in the developing brain may facilitate the onset of ASD, with an association found in six out of eight studies between the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) by the pregnant mother and the development of ASD in the child exposed to SSRI in the antenatal environment. The study could not definitively conclude SSRIs caused the increased risk for ASD due to the biases found in those studies, and the authors called for more definitive, better conducted studies.[185] Confounding by indication has since then been shown to be likely.[186] However, it is also hypothesized that SSRIs may help reduce symptoms of ASD and even positively affect brain development in some ASD patients.[126]
Diagnosis
Management
There is no treatment as such for autism,[187] and many sources advise that this is not an appropriate goal,[188][189] although treatment of co-occurring conditions remains an important goal.[190] There is no cure for autism as of 2022, nor can any of the known treatments significantly reduce brain mutations caused by autism, although those who require little-to-no support are more likely to experience a lessening of symptoms over time.[191][192][193] Several interventions can help children with autism,[194] and no single treatment is best, with treatment typically tailored to the child's needs.[195] Studies of interventions have methodological problems that prevent definitive conclusions about efficacy;[196] however, the development of evidence-based interventions has advanced.[197]
The main goals of treatment are to lessen associated deficits and family distress, and to increase quality of life and functional independence. In general, higher IQs are correlated with greater responsiveness to treatment and improved treatment outcomes.[198][199] Behavioral, psychological, education, and/or skill-building interventions may be used to assist autistic people to learn life skills necessary for living independently,[200] as well as other social, communication, and language skills. Therapy also aims to reduce challenging behaviors and build upon strengths.[201]
Intensive, sustained special education programs and behavior therapy early in life may help children acquire self-care, language, and job skills.[195] Although evidence-based interventions for autistic children vary in their methods, many adopt a psychoeducational approach to enhancing cognitive, communication, and social skills while minimizing problem behaviors. While medications have not been found to help with core symptoms, they may be used for associated symptoms, such as irritability, inattention, or repetitive behavior patterns.[202]
Non-pharmacological interventions
Intensive, sustained special education or remedial education programs and behavior therapy early in life may help children acquire self-care, social, and job skills. Available approaches include applied behavior analysis, developmental models, structured teaching, speech and language therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy,[203] social skills therapy, and occupational therapy.[204] Among these approaches, interventions either treat autistic features comprehensively, or focus treatment on a specific area of deficit.[199] Generally, when educating those with autism, specific tactics may be used to effectively relay information to these individuals. Using as much social interaction as possible is key in targeting the inhibition autistic individuals experience concerning person-to-person contact. Additionally, research has shown that employing semantic groupings, which involves assigning words to typical conceptual categories, can be beneficial in fostering learning.[205]
There has been increasing attention to the development of evidence-based interventions for autistic young children. Three theoretical frameworks outlined for early childhood intervention include applied behavior analysis (ABA), the developmental social-pragmatic model (DSP) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).[203][199] Although ABA therapy has a strong evidence base, particularly in regard to early intensive home-based therapy, ABA's effectiveness may be limited by diagnostic severity and IQ of the person affected by ASD.[206] The Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology has published a paper deeming two early childhood interventions "well-established": individual comprehensive ABA, and focused teacher-implemented ABA combined with DSP.[199]
Another evidence-based intervention that has demonstrated efficacy is a parent training model, which teaches parents how to implement various ABA and DSP techniques themselves.[199] Various DSP programs have been developed to explicitly deliver intervention systems through at-home parent implementation.
In October 2015, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) proposed new evidence-based recommendations for early interventions in ASD for children under 3.[207] These recommendations emphasize early involvement with both developmental and behavioral methods, support by and for parents and caregivers, and a focus on both the core and associated symptoms of ASD.[207] However, a Cochrane review found no evidence that early intensive behavioral intervention (EIBI) is effective in reducing behavioral problems associated with autism in most autistic children but did help improve IQ and language skills.[208] The Cochrane review did acknowledge that this may be due to the low quality of studies currently available on EIBI and therefore providers should recommend EIBI based on their clinical judgement and the family's preferences.[208] No adverse effects of EIBI treatment were found.[208] A meta-analysis in that same database indicates that due to the degrees of severity in ASD, there is variable responses to differing early ABA interventions.[209]
Generally speaking, treatment of ASD focuses on behavioral and educational interventions to target its two core symptoms: social communication deficits and restricted, repetitive behaviors.[210] If symptoms continue after behavioral strategies have been implemented, some medications can be recommended to target specific symptoms or co-existing problems such as restricted and repetitive behaviors (RRBs), anxiety, depression, hyperactivity/inattention and sleep disturbance.[210] Melatonin for example can be used for sleep problems.[211]
While there are a number of parent-mediated behavioral therapies to target social communication deficits in children with autism, there is uncertainty regarding the efficacy of interventions to treat RRBs.[212]
Education

Educational interventions often used include applied behavior analysis (ABA), developmental models, structured teaching, speech and language therapy and social skills therapy.[195] Among these approaches, interventions either treat autistic features comprehensively, or focalize treatment on a specific area of deficit.[197]
The quality of research for early intensive behavioral intervention (EIBI)—a treatment procedure incorporating over thirty hours per week of the structured type of ABA that is carried out with very young children—is currently low, and more vigorous research designs with larger sample sizes are needed.[208] Two theoretical frameworks outlined for early childhood intervention include structured and naturalistic ABA interventions, and developmental social pragmatic models (DSP).[197] One interventional strategy utilizes a parent training model, which teaches parents how to implement various ABA and DSP techniques, allowing for parents to disseminate interventions themselves.[197] Various DSP programs have been developed to explicitly deliver intervention systems through at-home parent implementation. Despite the recent development of parent training models, these interventions have demonstrated effectiveness in numerous studies, being evaluated as a probable efficacious mode of treatment.[197] Early, intensive ABA therapy has demonstrated effectiveness in enhancing communication and adaptive functioning in preschool children;[195] it is also well-established for improving the intellectual performance of that age group.[195]
A 2018 Cochrane meta-analysis database concludes how some recent research is beginning to suggest that because of the heterology of ASD, there is two varying ABA teaching approaches to acquiring spoken language: children with more general expressive language delays respond sufficiently to the naturalistic approach, whereas children with receptive language delays require discrete trial training—a structured and intensive form of ABA.[209]
Similarly, a teacher-implemented intervention that utilizes a more naturalistic form of ABA combined with a developmental social pragmatic approach has been found to be beneficial in improving social-communication skills in young children, although there is less evidence in its treatment of global symptoms.[197] Neuropsychological reports are often poorly communicated to educators, resulting in a gap between what a report recommends and what education is provided.[214] The appropriateness of including children with varying severity of autism spectrum disorders in the general education population is a subject of current debate among educators and researchers.[215]
Pharmacological interventions
Medications may be used to treat ASD symptoms that interfere with integrating a child into home or school when behavioral treatment fails.[216] They may also be used for associated health problems, such as ADHD or anxiety.[216] However, their routine prescription for the core features of ASD is not recommended.[217] More than half of US children diagnosed with ASD are prescribed psychoactive drugs or anticonvulsants, with the most common drug classes being antidepressants, stimulants, and antipsychotics.[218][219] The atypical antipsychotic drugs risperidone and aripiprazole are FDA-approved for treating associated aggressive and self-injurious behaviors.[202][220] However, their side effects must be weighed against their potential benefits, and autistic people may respond atypically.[202] Side effects may include weight gain, tiredness, drooling, and aggression.[202] There is some emerging data that show positive effects of aripiprazole and risperidone on restricted and repetitive behaviors (i.e., stimming; e.g., flapping, twisting, complex whole-body movements),[217] but due to the small sample size and different focus of these studies and the concerns about its side effects, antipsychotics are not recommended as primary treatment of RRBs.[221] SSRI antidepressants, such as fluoxetine and fluvoxamine, have been shown to be effective in reducing repetitive and ritualistic behaviors, while the stimulant medication methylphenidate is beneficial for some children with co-morbid inattentiveness or hyperactivity.[195] There is scant reliable research about the effectiveness or safety of drug treatments for adolescents and adults with ASD.[medical citation needed] No known medication relieves autism's core symptoms of social and communication impairments.[202]
Alternative medicine
A multitude of researched alternative therapies have also been implemented. Many have resulted in harm to autistic people.[204] A 2020 systematic review on adults with autism has provided emerging evidence for decreasing stress, anxiety, ruminating thoughts, anger, and aggression through mindfulness-based interventions for improving mental health.[222]
Although popularly used as an alternative treatment for autistic people, as of 2018[update] there is no good evidence to recommend a gluten- and casein-free diet as a standard treatment.[223][224][225] A 2018 review concluded that it may be a therapeutic option for specific groups of children with autism, such as those with known food intolerances or allergies, or with food intolerance markers. The authors analyzed the prospective trials conducted to date that studied the efficacy of the gluten- and casein-free diet in children with ASD (4 in total). All of them compared gluten- and casein-free diet versus normal diet with a control group (2 double-blind randomized controlled trials, 1 double-blind crossover trial, 1 single-blind trial). In two of the studies, whose duration was 12 and 24 months, a significant improvement in ASD symptoms (efficacy rate 50%) was identified. In the other two studies, whose duration was 3 months, no significant effect was observed.[223] The authors concluded that a longer duration of the diet may be necessary to achieve the improvement of the ASD symptoms.[223] Other problems documented in the trials carried out include transgressions of the diet, small sample size, the heterogeneity of the participants and the possibility of a placebo effect.[225][226][227] In the subset of people who have gluten sensitivity there is limited evidence that suggests that a gluten-free diet may improve some autistic behaviors.[228][229][230]
The preference that autistic children have for unconventional foods can lead to reduction in bone cortical thickness with this risk being greater in those on casein-free diets, as a consequence of the low intake of calcium and vitamin D; however, suboptimal bone development in ASD has also been associated with lack of exercise and gastrointestinal disorders.[231] In 2005, botched chelation therapy killed a five-year-old child with autism.[232][233] Chelation is not recommended for autistic people since the associated risks outweigh any potential benefits.[234] Another alternative medicine practice with no evidence is CEASE therapy, a pseudoscientific mixture of homeopathy, supplements, and 'vaccine detoxing'.[235]
Results of a systematic review on interventions to address health outcomes among autistic adults found emerging evidence to support mindfulness-based interventions for improving mental health. This includes decreasing stress, anxiety, ruminating thoughts, anger, and aggression.[236] An updated Cochrane review (2022) found evidence that music therapy likely improves social interactions, verbal communication, and non-verbal communication skills.[237] There has been early research looking at hyperbaric treatments in children with autism.[238] Studies on pet therapy have shown positive effects.[239]
Prevention
While infection with rubella during pregnancy causes fewer than 1% of cases of autism,[240] vaccination against rubella can prevent many of those cases.[241]
Prognosis
There is currently no evidence of a cure for autism.[195][101] The degree of symptoms can decrease, occasionally to the extent that people lose their diagnosis of ASD;[242][243] this occurs sometimes after intensive treatment[244] and sometimes not. It is not known how often this outcome happens,[245] with reported rates in unselected samples ranging from 3% to 25%.[242][243] Although core difficulties tend to persist, symptoms often become less severe with age.[111] Acquiring language before age six, having an IQ above 50, and having a marketable skill all predict better outcomes; independent living is unlikely in autistic people with higher support needs.[246]
Developmental course
There are two possible developmental courses of ASD. One course of development is more gradual in nature, with symptoms appearing fairly early in life and persisting.[247] A second course of development is characterized by normal or near-normal development before onset of regression or loss of skills, which is known as regressive autism.[248]
Gradual autism development
Most parents report that the onset of autism features appear within the first or second year of life.[249][250] This course of development is fairly gradual, in that parents typically report concerns in development over the first two years of life and diagnosis can be made around 3–4 years of age.[247] Overt features gradually begin after the age of six months, become established by age two or three years,[251] and tend to continue through adulthood, although often in more muted form.[111] Some of the early signs of ASDs in this course include decreased attention at faces, failure to obviously respond when name is called, failure to show interests by showing or pointing, and delayed imaginative play.[252]
Regressive autism development
Regressive autism occurs when a child appears to develop typically but then starts to lose speech and social skills and is subsequently diagnosed with ASD.[134] Other terms used to describe regression in children with autism are autism with regression, autistic regression, setback-type autism, and acquired autistic syndrome.[253]
Within the regressive autism developmental course, there are two patterns. The first pattern is when developmental losses occur in the first 15 months to 3 years.[254][255] The second pattern, childhood disintegrative disorder (a diagnosis now included under ASD in the DSM, but not the ICD), is characterized by regression after normal development in the first 3 to 4, or even up to 9 years of life.[256]
After the regression, the child follows the standard pattern of autistic neurological development. The term regressive autism refers to the appearance that neurological development has reversed; it is actually only the affected developmental skills, rather than the neurology as a whole, that regresses.
Usually, the apparent onset of regressive autism can be surprising and distressing to parents, who often initially suspect severe hearing loss.[257] Attribution of regression to environmental stress factors may result in a delay in diagnosis.[65]
There is no standard definition for regression.[253] Some children show a mixture of features, with some early delays and some later losses; and there is evidence of a continuous spectrum of behaviors, rather than, or in addition to, a black-and-white distinction, between autism with and without regression.[258] There are several intermediate types of development, which do not neatly fit into either the traditional early onset or the regressive categories, including mixtures of early deficits, failures to progress, subtle diminishment, and obvious losses.
Regression may occur in a variety of domains, including communication, social, cognitive, and self-help skills; however, the most common regression is loss of language.[259][254][255] Some children lose social development instead of language; some lose both.[258] Skill loss may be quite rapid, or may be slow and preceded by a lengthy period of no skill progression; the loss may be accompanied by reduced social play or increased irritability.[253] The temporarily acquired skills typically amount to a few words of spoken language, and may include some rudimentary social perception.[258]
The prevalence of regression varies depending on the definition used.[258] If regression is defined strictly to require loss of language, it is less common; if defined more broadly, to include cases where language is preserved but social interaction is diminished, it is more common.[258] Although regressive autism is often thought to be a less common (compared with gradual course of autism onset described above), this remains an area of ongoing debate;[259] some evidence suggests that a pattern of regressive autism may be more common than previously thought.[260] There are some who believe that regressive autism is simply early-onset autism which was recognized at a later date. Researchers have conducted studies to determine whether regressive autism is a distinct subset of ASD, but the results of these studies have contradicted one another.[134]
Differential outcomes
There continues to be a debate over the differential outcomes based on these two developmental courses. Some studies suggest that regression is associated with poorer outcomes and others report no differences between those with early gradual onset and those who experience a regression period.[261] While there is conflicting evidence surrounding language outcomes in autism, some studies have shown that cognitive and language abilities at age 2+1⁄2 may help predict language proficiency and production after age 5.[262] Overall, the literature stresses the importance of early intervention in achieving positive longitudinal outcomes.[263]
Academic performance
The examples and perspective in this section deal primarily with the United States and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (April 2022) |
The number of students identified and served as eligible for autism services in the United States has increased from 5,413 children in 1991–1992 to 370,011 children in the 2010–2011 academic school year.[264] The United States Department of Health and Human Services reported approximately 1 in 68 children are diagnosed with ASD at age 8 although onset is typically between ages 2 and 4.[264]
The increasing number of students diagnosed with ASD in the schools presents significant challenges to teachers, school psychologists, and other school professionals.[264] These challenges include developing a consistent practice that best support the social and cognitive development of the increasing number of autistic students.[264] Although there is considerable research addressing assessment, identification, and support services for autistic children, there is a need for further research focused on these topics within the school context.[264] Further research on appropriate support services for students with ASD will provide school psychologists and other education professionals with specific directions for advocacy and service delivery that aim to enhance school outcomes for students with ASD.[264]
Attempts to identify and use best intervention practices for students with autism also pose a challenge due to over dependence on popular or well-known interventions and curricula.[264] Some evidence suggests that although these interventions work for some students, there remains a lack of specificity for which type of student, under what environmental conditions (one-on-one, specialized instruction or general education) and for which targeted deficits they work best.[264] More research is needed to identify what assessment methods are most effective for identifying the level of educational needs for students with ASD. Additionally, children living in higher resources settings in the United States tend to experience earlier ASD interventions than children in lower resource settings (e.g. rural areas).[265]
A difficulty for academic performance in students with ASD is the tendency to generalize learning.[59] Learning is different for each student, which is the same for students with ASD. To assist in learning, accommodations are commonly put into place for students with differing abilities. The existing schema of these students works in different ways and can be adjusted to best support the educational development for each student.[266]
The cost of educating a student with ASD in the US would be about $20,600 while educating an average student would be about $12,000.[267]
Though much of the focus on early childhood intervention for ASD has centered on high-income countries like the United States, some of the most significant unmet needs for autistic individuals are in low- and middle-income countries.[265] In these contexts, research has been more limited but there is evidence to suggest that some comprehensive care plans can be successfully delivered by non-specialists in schools and in the community.[265]
Employment
The examples and perspective in this section deal primarily with the United States and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (April 2022) |
Many autistic people face significant obstacles in transitioning to adulthood.[268] Compared to the general population, autistic people are more likely to be unemployed and to have never had a job. About half of people in their 20s with autism are not employed.[269] Some autistic adults are unable to live independently.[270]
In the United States, about half of people in their 20s with autism are unemployed, and one third of those with graduate degrees may be unemployed.[271] While employers state hiring concerns about productivity and supervision, experienced employers of autistics give positive reports of above average memory and detail orientation as well as a high regard for rules and procedure in autistic employees.[271] The majority of the economic burden of autism is caused by lost productivity in the job market.[272] From the perspective of the social model of disability, much of this unemployment is caused by the lack of understanding from employers and coworkers.[273][274] Adding content related to autism in existing diversity training can clarify misconceptions, support employees, and help provide new opportunities for autistic people.[275] As of 2021, the potential for new autism employment initiatives by major employers in the United States continue to grow. The most high-profile autism initiative in the United States, "Autism at Work" grew to 20 of the largest companies in the United States.[276] However, special hiring programs remain largely limited to entry-level technology positions, such as software testing, and exclude those who have talents outside of technology. An alternative approach is systemic neurodiversity inclusion. Developing organizational systems with enough flexibility and fairness to include autistic employees improves the work experience of all employees.[277][278]
Epidemiology

The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates about 1 in 100 children have autism.[5][279] The number of people diagnosed has increased considerably since the 1990s, which may be partly due to increased recognition of the condition.[280]
While rates of ASD are consistent across cultures, they vary greatly by gender, with boys diagnosed far more frequently than girls: 1 in 70 boys, but only 1 in 315 girls at eight years of age.[281] Girls, however, are more likely to have associated cognitive impairment, suggesting that less severe forms of ASD are likely being missed in girls and women.[282] Prevalence differences may be a result of gender differences in expression of clinical symptoms, with women and girls with autism showing less atypical behaviors and, therefore, less likely to receive an ASD diagnosis.[283]
Using DSM-5 criteria, 92% of the children diagnosed per DSM-IV with one of the disorders which is now considered part of ASD will still meet the diagnostic criteria of ASD. However, if both ASD and the social (pragmatic) communication disorder categories of DSM-5 are combined, the prevalence of autism is mostly unchanged from the prevalence per the DSM-IV criteria. The best estimate for prevalence of ASD is 0.7% or 1 child in 143 children.[284] Relatively mild forms of autism, such as Aspergers as well as other developmental disorders, are included in the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria.[285] ASD rates were constant between 2014 and 2016 but twice the rate compared to the time period between 2011 and 2014 (1.25 vs 2.47%). A Canadian meta-analysis from 2019 confirmed these effects as the profiles of people diagnosed with autism became less and less different from the profiles of the general population.[286] In the US, the rates for diagnosed ASD have been steadily increasing since 2000 when records began being kept.[287] While it remains unclear whether this trend represents a true rise in incidence, it likely reflects changes in ASD diagnostic criteria, improved detection, and increased public awareness of autism.[288] In 2012, the NHS estimated that the overall prevalence of autism among adults aged 18 years and over in the UK was 1.1%.[289] A 2016 survey in the United States reported a rate of 25 per 1,000 children for ASD.[290] It is important to note that rates of autism are poorly understood in many low- and middle-income countries, which affects the accuracy of global ASD prevalence estimates,[291] but it is thought that most autistic individuals live in low- and middle-income countries.[265]
In the UK, from 1998 to 2018, the autism diagnoses increased by 787%.[280] This increase is largely attributable to changes in diagnostic practices, referral patterns, availability of services, age at diagnosis, and public awareness[292][293][294] (particularly among women),[280] though unidentified environmental risk factors cannot be ruled out.[295] The available evidence does not rule out the possibility that autism's true prevalence has increased;[292] a real increase would suggest directing more attention and funding toward psychosocial factors and changing environmental factors instead of continuing to focus on genetics.[296] It has been established that vaccination is not a risk factor for autism and is not a cause of any increase in autism prevalence rates, if any change in the rate of autism exists at all.[153]
Males have higher likelihood of being diagnosed with ASD than females. The sex ratio averages 4.3:1 and is greatly modified by cognitive impairment: it may be close to 2:1 with intellectual disability and more than 5.5:1 without.[139] Several theories about the higher prevalence in males have been investigated, but the cause of the difference is unconfirmed;[297] one theory is that females are underdiagnosed.[298]
The risk of developing autism is greater with older fathers than with older mothers; two potential explanations are the known increase in mutation burden in older sperm, and the hypothesis that men marry later if they carry genetic liability and show some signs of autism.[22] Most professionals believe that race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic background do not affect the occurrence of autism.[299]
United States
As of 2020[update], CDC prevalence reports show that 1 in 36 children (approximately 4% of boys and 1% of girls) in the United States have a diagnosis of ASD.[300]
History
Society and culture
An autistic culture has emerged, accompanied by the autistic rights and neurodiversity movements, that argues autism should be accepted as a difference to be accommodated instead of cured,[301][302][303][304][305] although a minority of autistic people might still accept a cure.[306] Worldwide, events related to autism include World Autism Awareness Day, Autism Sunday, Autistic Pride Day, Autreat, and others.[307][308][309][310] Social-science scholars study those with autism in hopes to learn more about "autism as a culture, transcultural comparisons ... and research on social movements."[311] Many autistic people have been successful in their fields.[312]
Neurodiversity movement
Some autistic people, as well as a growing number of researchers,[313] have advocated a shift in attitudes toward the view that autism spectrum disorder is a difference, rather than a disease that must be treated or cured.[314][315] Critics have bemoaned the entrenchment of some of these groups' opinions.[316][317][318][319]
The neurodiversity movement and the autism rights movement are social movements within the context of disability rights, emphasizing the concept of neurodiversity, which describes the autism spectrum as a result of natural variations in the human brain rather than a disorder to be cured.[303] The autism rights movement advocates for including greater acceptance of autistic behaviors; therapies that focus on coping skills rather than imitating the behaviors of those without autism;[320] and the recognition of the autistic community as a minority group.[320][321]
Autism rights or neurodiversity advocates believe that the autism spectrum is genetic and should be accepted as a natural variation in the human genome.[303] These movements are not without detractors; a common argument against neurodiversity activists is that most of them have relatively low support needs, or are self-diagnosed, and do not represent the views of autistic people with higher support needs.[321][322][323]
The concept of neurodiversity is contentious in autism advocacy and research groups and has led to infighting.[324][325]
Symbols and flags


Over the years, multiple organizations have tried to capture the essence of autism in symbols. In 1963, the board for the National Autistic Society, led by Gerald Gasson, proposed the "puzzle piece" as a symbol for autism, because it fit their view of autism as a "puzzling condition".[326] In 1999, the Autism Society adopted the puzzle ribbon as the universal sign of autism awareness.[326] In 2004, neurodiversity advocates Amy and Gwen Nelson conjured the "rainbow infinity symbol". It was initially the logo for their website, Aspies for Freedom. Nowadays, the prismatic colors are often associated with the neurodiversity movement in general.[327] The autistic spectrum has also been symbolized by the infinity symbol itself.[328] In 2018, Julian Morgan wrote the article "Light It Up Gold", a response to Autism Speaks's "Light It Up Blue" campaign, launched in 2007.[329][330] Aurum is Latin for gold,[327] and gold has been used to symbolize autism, since both words start with "Au". Though a consensus for a flag to unite autism and neurodiversity has not yet been established, one has gained traction on Reddit.[331] The flag implements a gradient to represent the Pride Movement and incorporates a golden infinity symbol as its focal point.[332] While flags are symbols of solidarity, they may trigger negative associations, such as apparent rivalry among two or more flags.[333] For this reason, flags are sought that can be tailored to the personal preferences of any neurotype.[334][335]

Caregivers
Families who care for an autistic child face added stress from a number of different causes.[66][336] Parents may struggle to understand the diagnosis and to find appropriate care options. They often take a negative view of the diagnosis, and may struggle emotionally.[337] More than half of parents over age 50 are still living with their child, as about 85% of autistic people have difficulties living independently.[338] Some studies also find decreased earnings among parents who care for autistic children.[339][340] Siblings of children with ASD report greater admiration and less conflict with the affected sibling than siblings of unaffected children, like siblings of children with Down syndrome. But they reported lower levels of closeness and intimacy than siblings of children with Down syndrome; siblings of people with ASD have a greater risk of negative well-being and poorer sibling relationships as adults.[341]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Bonati M, Cartabia M, Clavenna A (January 2022). "Still too much delay in recognition of autism spectrum disorder". Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences. 31 (e1). Cambridge University Press: e1. doi:10.1017/S2045796021000822. LCCN 2011243374. OCLC 727338545. PMC 8786613. PMID 35012703. S2CID 245851335.
- ^ Pezzimenti, F.; Han, G. T.; Vasa, R. A.; Gotham, K. (2019). "Depression in Youth with Autism Spectrum Disorder". Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 28 (3): 397–409. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2019.02.009. PMC 6512853. PMID 31076116.
- ^ "At the intersection of autism and trauma". 26 September 2018.
- ^ "Autism's drug problem". 19 April 2017.
- ^ a b Zeidan, Jinan; Fombonne, Eric; Scorah, Julie; Ibrahim, Alaa; Durkin, Maureen S.; Saxena, Shekhar; Yusuf, Afiqah; Shih, Andy; Elsabbagh, Mayada (15 May 2022). "Global prevalence of autism: A systematic review update". Autism Research. 15 (5): 778–790. doi:10.1002/aur.2696. ISSN 1939-3806. PMC 9310578. PMID 35238171.
- ^ Pellicano E, den Houting J (April 2022). "Annual Research Review: Shifting from 'normal science' to neurodiversity in autism science". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 63 (4): 381–396. doi:10.1111/jcpp.13534. eISSN 1469-7610. ISSN 0021-9630. OCLC 01307942. PMC 9298391. PMID 34730840. S2CID 241118562.
- ^ "Welcome to the Autistic Community". Autistic Self Advocacy Network. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ Bailin A (6 June 2019). "Clearing Up Some Misconceptions about Neurodiversity". Scientific American Blog Network. Nature America, Inc. Archived from the original on 29 June 2019. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ^ Robison JE (2020). "My Time with Autism Speaks". In Kapp SK (ed.). Autistic Community and the Neurodiversity Movement. Singapore: Springer. pp. 221–232. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-8437-0_16. ISBN 978-981-13-8437-0. S2CID 210496353. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Opar, Alisa (24 April 2019). "In search of truce in the autism wars". Spectrum. Simons Foundation. doi:10.53053/VRKL4748. S2CID 249140855.
- ^ Mandy W, Lai MC (March 2016). "Annual Research Review: The role of the environment in the developmental psychopathology of autism spectrum condition". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 57 (3): 271–292. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12501. eISSN 1469-7610. ISSN 0021-9630. OCLC 01307942. PMID 26782158.
- ^ Rosen NE, Lord C, Volkmar FR (December 2021). "The Diagnosis of Autism: From Kanner to DSM-III to DSM-5 and Beyond". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 51 (12): 4253–4270. doi:10.1007/s10803-021-04904-1. PMC 8531066. PMID 33624215.
- ^ Losh M, Adolphs R, Piven J (2011). "The Broad Autism Phenotype". Autism Spectrum Disorders. Oxford University Press. pp. 457–476. doi:10.1093/med/9780195371826.003.0031. ISBN 978-0-19-996521-2.
- ^ Chapman R, Veit W (November 2021). "Correction to: The essence of autism: fact or artefact?". Molecular Psychiatry. 26 (11): 7069. doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01057-6. PMID 34697454. S2CID 239771302.
- ^ Wazana A, Bresnahan M, Kline J (June 2007). "The autism epidemic: fact or artifact?". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 46 (6): 721–730. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e31804a7f3b. PMID 17513984.
- ^ a b DeStefano F, Shimabukuro TT (September 2019). "The MMR Vaccine and Autism". Annual Review of Virology. 6 (1): 585–600. doi:10.1146/annurev-virology-092818-015515. PMC 6768751. PMID 30986133.
- ^ Kirkham P (1 April 2017). "'The line between intervention and abuse' – autism and applied behaviour analysis". History of the Human Sciences. 30 (2): 107–126. doi:10.1177/0952695117702571. ISSN 0952-6951. S2CID 152017417.
- ^ "Medication Treatment for Autism". www.nichd.nih.gov/. 19 April 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ "Why Asperger's Syndrome is no longer listed in the DSM".
- ^ "Diagnostic Criteria | Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) | NCBDDD | CDC". 2 November 2022.
- ^ "ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics".
- ^ a b Geschwind DH (October 2008). "Autism: many genes, common pathways?". Cell. 135 (3): 391–395. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.016. PMC 2756410. PMID 18984147.
- ^ Happé F (1999). "Understanding assets and deficits in autism: why success is more interesting than failure" (PDF). Psychologist. 12 (11): 540–547. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 May 2012.
- ^ Wing L (December 1997). "The autistic spectrum". Lancet. 350 (9093): 1761–1766. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)09218-0. PMID 9413479. S2CID 7165992.
- ^ "Diagnostic criteria - a guide for all audiences". National Autistic Society. Retrieved 1 December 2022.
- ^ a b Pickett D, Anderson RN (18 July 2018). Status on ICD-11: The WHO Launch (PDF) (Report). CDC/NCHS.
- ^ "ICD vs. DSM". APA Monitor. Vol. 40, no. 9. American Psychological Association. 2009. p. 63.
- ^ Mezzich JE (2002). "International surveys on the use of ICD-10 and related diagnostic systems". Psychopathology. 35 (2–3): 72–75. doi:10.1159/000065122. PMID 12145487. S2CID 35857872.
- ^ Goldberg D (January 2010). "The classification of mental disorder: a simpler system for DSM–V and ICD–11". Advances in Psychiatric Treatment. 16 (1): 14–19. doi:10.1192/apt.bp.109.007120.
- ^ "WHO releases new International Classification of Diseases (ICD 11)". World Health Organisation (Press Release). Retrieved 29 October 2021.
- ^ ICD-11.
- ^ Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Arlington County: American Psychiatric Association, 18 May 2013, doi:10.1176/APPI.BOOKS.9780890425596, OCLC 830807378, OL 27587204M, Wikidata Q3064664
- ^ a b c d e DSM-5-TR.
- ^ DSM-5-TR, "Autism spectrum disorder encompasses disorders previously referred to as early infantile autism, childhood autism, Kanner's autism, high-functioning autism, atypical autism, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified, childhood disintegrative disorder, and Asperger's disorder".
- ^ Kulage KM, Smaldone AM, Cohn EG (August 2014). "How will DSM-5 affect autism diagnosis? A systematic literature review and meta-analysis". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 44 (8): 1918–32. doi:10.1007/s10803-014-2065-2. PMID 24531932. S2CID 18865395.
- ^ "DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria". U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee. Retrieved 17 May 2017.
- ^ "F84. Pervasive developmental disorders". ICD-10: International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems: Tenth Revision. World Health Organization. 2007. Archived from the original on 21 April 2013. Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- ^ Loukusa S (2021). "Autism Spectrum Disorder". In Cummings L (ed.). Handbook of pragmatic language disorders : complex and underserved populations. Cham, Switzerland: Springer. pp. 45–78. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-74985-9_3. ISBN 978-3-030-74984-2. OCLC 1269056169. S2CID 239160368.
- ^ Pinel JP (2011). Biopsychology (8th ed.). Boston, Massachusetts: Pearson. p. 235. ISBN 978-0-205-03099-6. OCLC 1085798897.
- ^ Hollander E, Hagerman R, Fein D, eds. (2018). Autism Spectrum Disorders. American Psychiatric Association. Chapter 6: Cognitive Assessment. doi:10.1176/appi.books.9781615371921. ISBN 978-1-61537-192-1. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ Autism spectrum disorder in adults: diagnosis and management, NICE, 14 June 2021, CG142, retrieved 24 October 2021
- ^ "About autism spectrum disorder (ASD)". Government of Canada. 18 January 2016. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "What are the signs and symptoms of ASD?". Government of Canada. 18 January 2016. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities (25 March 2020). "What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 24 October 2021.
- ^ Piven J, Palmer P, Jacobi D, Childress D, Arndt S (February 1997). "Broader autism phenotype: evidence from a family history study of multiple-incidence autism families". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 154 (2): 185–190. doi:10.1176/ajp.154.2.185. PMID 9016266.
- ^ CDC (31 March 2022). "Basics About Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) | NCBDDD | CDC". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 15 September 2022.
- ^ Barnhill GP (2007). "Outcomes in adults with Asperger syndrome". Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities. 22 (2): 116–126. doi:10.1177/10883576070220020301. S2CID 1355689.
- ^ Howlin P, Moss P (May 2012). "Adults with autism spectrum disorders". Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 57 (5): 275–83. doi:10.1177/070674371205700502. PMID 22546059. S2CID 44544407.
- ^ Emily Harrison (25 January 2021). "Autism Myth #6: People with Autism Don't Have Empathy". Retrieved 5 January 2023.
- ^ Milton, Damian; Gurbuz, Emine; López, Beatriz (November 2022). "The 'double empathy problem': Ten years on". Autism. 26 (8): 1901–1903. doi:10.1177/13623613221129123. ISSN 1362-3613. PMID 36263746. S2CID 253020669.
- ^ Crompton, Catherine J.; Debrabander, Kilee; Heasman, Brett; Milton, Damian; Sasson, Noah J. (2021). "Double Empathy: Why Autistic People Are Often Misunderstood". Frontiers for Young Minds. 9. doi:10.3389/frym.2021.554875.
- ^ Frye RE (August 2018). "Social Skills Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Potential Biological Origins and Progress in Developing Therapeutic Agents". CNS Drugs. 32 (8): 713–734. doi:10.1007/s40263-018-0556-y. PMC 6105175. PMID 30105528.
- ^ a b c d e f g Augustyn M. "Autism spectrum disorder: Clinical features". UpToDate. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ Bird G, Cook R (July 2013). "Mixed emotions: the contribution of alexithymia to the emotional symptoms of autism". Translational Psychiatry. 3 (7): e285. doi:10.1038/tp.2013.61. PMC 3731793. PMID 23880881.
- ^ National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities (29 June 2020). "Diagnostic Criteria: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d "Autism Spectrum Disorder: Communication Problems in Children". NIDCD. 18 August 2015. Retrieved 17 December 2017.
- ^ a b Vicker B. "Social communication and language characteristics associated with high-functioning, verbal children and adults with autism spectrum disorder". Indiana Resource Center for Autism. Retrieved 17 December 2017.
- ^ a b Lawson W (2001). Understanding and Working With the Spectrum of Autism: An Insider's View. London UK, & Philadelphia PA: Jessica Kingsley Publishers. pp. 33. ISBN 978-1853029714.
- ^ a b Fusaroli R, Lambrechts A, Bang D, Bowler DM, Gaigg SB (March 2017). "Is voice a marker for Autism spectrum disorder? A systematic review and meta-analysis" (PDF). Autism Research. 10 (3): 384–407. doi:10.1002/aur.1678. PMID 27501063. S2CID 13772771.
- ^ "Autism: Overview". American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. Retrieved 17 December 2017.
- ^ Cohen D, Grandin T (25 October 2005). "Temple Grandin: 'I'm an anthropologist from Mars'". The Guardian. Kings Place, London: Scott Trust. eISSN 1756-3224. ISSN 0261-3077. OCLC 60623878. Archived from the original on 9 November 2013. Retrieved 6 July 2022.
- ^ Keating CT, Cook JL (July 2020). "Facial expression production and recognition in autism spectrum disorders: a shifting landscape". Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am (Review). 29 (3): 557–571. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2020.02.006. PMID 32471602.
- ^ a b c Tager-Flusberg H, Caronna E (June 2007). "Language disorders: autism and other pervasive developmental disorders". Pediatric Clinics of North America. 54 (3): 469–81, vi. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2007.02.011. PMID 17543905. S2CID 13615727.
- ^ a b c d Johnson CP, Myers SM (November 2007). "Identification and evaluation of children with autism spectrum disorders". Pediatrics. 120 (5): 1183–1215. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2361. PMID 17967920. Archived from the original on 8 February 2009.
- ^ a b Volkmar FR, Paul R, Pelphrey KA, Rogers SJ, eds. (2014). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders: Volume Two: Assessment, Interventions, and Policy. Vol. 2 (4th ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons. p. 301. ISBN 978-1-118-28220-5. LCCN 2013034363. OCLC 946133861. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- ^ National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities (26 February 2015). "Signs & Symptoms: Autism Spectrum Disorder". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 10 March 2015. (Also available in Spanish.)
- ^ "Engaging people on the autism spectrum". Autism Spectrum Australia. 7 October 2013. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020.
- ^ Hinerman PS (1983). Teaching Autistic Children to Communicate. Rockville, Maryland: Aspens System Corporation. p. 180. ISBN 978-0-89443-884-4.
- ^ a b c d Lord C, Elsabbagh M, Baird G, Veenstra-Vanderweele J (August 2018). "Autism spectrum disorder". Lancet. 392 (10146): 508–520. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31129-2. PMC 7398158. PMID 30078460. S2CID 51922565.
- ^ DSM-5-TR, "Hyper- or hyporeactivity to sensory input or unusual interest in sensory aspects of the environment (e.g., apparent indifference to pain/temperature, adverse response to specific sounds or textures, excessive smelling or touching of objects, visual fascination with lights or movement)".
- ^ a b Lam KS, Aman MG (May 2007). "The Repetitive Behavior Scale-Revised: independent validation in individuals with autism spectrum disorders". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 37 (5): 855–866. doi:10.1007/s10803-006-0213-z. PMID 17048092. S2CID 41034513.
- ^ a b Minshawi NF, Hurwitz S, Fodstad JC, Biebl S, Morriss DH, McDougle CJ (April 2014). "The association between self-injurious behaviors and autism spectrum disorders". Psychology Research and Behavior Management. 7: 125–36. doi:10.2147/PRBM.S44635. PMC 3990505. PMID 24748827.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c d Oliver C, Richards C (October 2015). "Practitioner Review: Self-injurious behaviour in children with developmental delay" (PDF). J Child Psychol Psychiatry (Review). 56 (10): 1042–54. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12425. PMID 25916173.
- ^ Flowers J, Lantz J, Hamlin T, Simeonsson RJ (August 2020). "Associated Factors of Self-injury Among Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder in a Community and Residential Treatment Setting". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 50 (8): 2987–3004. doi:10.1007/s10803-020-04389-4. PMID 32056114. S2CID 211111895.
- ^ a b Filipek PA, Accardo PJ, Baranek GT, Cook EH, Dawson G, Gordon B, et al. (December 1999). "The screening and diagnosis of autistic spectrum disorders". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 29 (6): 439–484. doi:10.1023/A:1021943802493. PMID 10638459. S2CID 145113684. This paper represents a consensus of representatives from nine professional and four parent organizations in the US.
- ^ Treffert DA (May 2009). "The savant syndrome: an extraordinary condition. A synopsis: past, present, future". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 364 (1522): 1351–1357. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0326. PMC 2677584. PMID 19528017.
- ^ Zhang Y, Han VZ (April 2018). "[Neurobiological mechanisms of autistic savant and acquired savant]" [Neurobiological mechanisms of autistic savant and acquired savant]. Sheng Li Xue Bao (in Chinese). 70 (2): 201–210. PMID 29691585.
- ^ Hughes JE, Ward J, Gruffydd E, Baron-Cohen S, Smith P, Allison C, Simner J (October 2018). "Savant syndrome has a distinct psychological profile in autism". Molecular Autism. 9: 53. doi:10.1186/s13229-018-0237-1. PMC 6186137. PMID 30344992.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Plaisted Grant K, Davis G (May 2009). "Perception and apperception in autism: rejecting the inverse assumption". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 364 (1522): 1393–1398. doi:10.1098/rstb.2009.0001. PMC 2677593. PMID 19528022.
- ^ a b Geschwind DH (2009). "Advances in autism". Annual Review of Medicine. 60: 367–380. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.60.053107.121225. PMC 3645857. PMID 19630577.
- ^ Happé F, Frith U (August 1996). "The neuropsychology of autism". Brain. 119 (4). OUP: 1377–1400. doi:10.1093/brain/119.4.1377. PMID 8813299.
- ^ Ben-Sasson A, Hen L, Fluss R, Cermak SA, Engel-Yeger B, Gal E (January 2009). "A meta-analysis of sensory modulation symptoms in individuals with autism spectrum disorders". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 39 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1007/s10803-008-0593-3. PMID 18512135. S2CID 5208889.
- ^ Gargot T, Archambault D, Chetouani M, Cohen D, Johal W, Anzalone SM (10 January 2022). "Automatic Assessment of Motor Impairments in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review" (PDF). Cognitive Computation. 14 (2): 624–659. doi:10.1007/s12559-021-09940-8. ISSN 1866-9964. S2CID 248326222.
- ^ Fournier KA, Hass CJ, Naik SK, Lodha N, Cauraugh JH (October 2010). "Motor coordination in autism spectrum disorders: a synthesis and meta-analysis". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 40 (10): 1227–1240. doi:10.1007/s10803-010-0981-3. PMID 20195737. S2CID 3469612.
- ^ Wang, Leah A. L.; Petrulla, Victoria; Zampella, Casey J.; Waller, Rebecca; Schultz, Robert T. (2022). "Gross motor impairment and its relation to social skills in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and two meta-analyses". Psychological Bulletin. 148 (3–4): 273–300. doi:10.1037/bul0000358. ISSN 1939-1455. PMC 9894569. PMID 35511567.
- ^ Dominick KC, Davis NO, Lainhart J, Tager-Flusberg H, Folstein S (2007). "Atypical behaviors in children with autism and children with a history of language impairment". Research in Developmental Disabilities. 28 (2). Elsevier: 145–162. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2006.02.003. eISSN 1873-3379. ISSN 0891-4222. PMID 16581226.
- ^ Van Der Miesen AI, Hurley H, De Vries AL (2016). "Gender dysphoria and autism spectrum disorder: A narrative review". International Review of Psychiatry. 28 (1): 70–80. doi:10.3109/09540261.2015.1111199. PMID 26753812. S2CID 20918937.
- ^ Glidden D, Bouman WP, Jones BA, Arcelus J (January 2016). "Gender Dysphoria and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review of the Literature". Sexual Medicine Reviews. 4 (1): 3–14. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2015.10.003. PMID 27872002. S2CID 3454600.
- ^ Weir E, Allison C, Baron-Cohen S (November 2021). "The sexual health, orientation, and activity of autistic adolescents and adults". Autism Research. 14 (11): 2342–2354. doi:10.17863/CAM.74771. PMID 34536071.
- ^ Handbook of autism and pervasive developmental disorder : assessment, diagnosis, and treatment (PDF). Autism and Child Psychopathology Series. Johnny L. Matson, Peter Sturmey. Cham: Springer Nature. 2022. p. 18. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-88538-0. ISBN 9783030885380. OCLC 1341298051. S2CID 251520573.
To date no one genetic feature or environmental cause has proven etiological in explaining most cases autism or has been able to account for rising rates of autism.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Sauer, Ann Katrin; Stanton, Janelle E.; Hans, Sakshi; Grabrucker, Andreas M. (2021). "Autism Spectrum Disorders: Etiology and Pathology". Written at Brisbane, Australia. In Grabrucker, Andreas M. (ed.). Autism spectrum disorders. Andreas M. Grabrucker. Brisbane: Exon Publications (published 20 August 2021). pp. 1–16. doi:10.36255/exonpublications.autismspectrumdisorders.2021.etiology. ISBN 9780645001785. OCLC 1280592589. PMID 34495611. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
The cause of ASD is unknown, but several genetic and non-genetic risk factors have been characterized that, alone or in combination, are implicated in the development of ASD.
- ^ Kałużna-Czaplińska, Joanna; Żurawicz, Ewa; Jóźwik-Pruska, Jagoda (2018). "Focus on the Social Aspect of Autism". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 48 (5). Springer Nature (published 29 November 2017): 1861–1867. doi:10.1007/s10803-017-3407-7. ISSN 1573-3432. PMC 5889772. PMID 29188587. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023.
Despite extensive ASD research lasting more than 60 years, its causes are still unknown.
- ^ Medavarapu, Srinivas; Marella, Lakshmi Lavanya; Sangem, Aneela; Kairam, Ram (2019). "Where is the Evidence? A Narrative Literature Review of the Treatment Modalities for Autism Spectrum Disorders". Cureus. 11 (1). Springer Nature (published 16 January 2019): e3901. doi:10.7759/cureus.3901. ISSN 2168-8184. PMC 6424545. PMID 30911457.
It is important to realize that the etiology of autism is unknown and at present, there is no cure, although there are interventions that may be effective in alleviating some symptoms and improving skills that may help autistic persons lead more productive lives.
- ^ a b Happé F, Ronald A (December 2008). "The 'fractionable autism triad': a review of evidence from behavioural, genetic, cognitive and neural research". Neuropsychology Review. 18 (4): 287–304. doi:10.1007/s11065-008-9076-8. PMID 18956240. S2CID 13928876.
- ^ a b Happé F, Ronald A, Plomin R (October 2006). "Time to give up on a single explanation for autism". Nature Neuroscience. 9 (10): 1218–1220. doi:10.1038/nn1770. PMID 17001340.
- ^ Tager-Flusberg H (2010). "The origins of social impairments in autism spectrum disorder: studies of infants at risk". Neural Networks. 23 (8–9): 1072–6. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2010.07.008. PMC 2956843. PMID 20800990.
- ^ Altevogt BM, Hanson SL, Leshner AI (June 2008). "Autism and the environment: challenges and opportunities for research". Pediatrics. 121 (6): 1225–1229. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-3000. PMID 18519493. S2CID 24595814. Archived from the original on 15 January 2010.
- ^ Reiss AL (January 2009). "Childhood developmental disorders: an academic and clinical convergence point for psychiatry, neurology, psychology and pediatrics". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 50 (1–2): 87–98. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.02046.x. eISSN 1469-7610. ISSN 0021-9630. OCLC 01307942. PMC 5756732. PMID 19220592.
- ^ Piggot J, Shirinyan D, Shemmassian S, Vazirian S, Alarcón M (November 2009). "Neural systems approaches to the neurogenetics of autism spectrum disorders". Neuroscience. 164 (1): 247–256. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.054. PMID 19482063. S2CID 207246176.
- ^ a b c Levy SE, Mandell DS, Schultz RT (November 2009). "Autism". Lancet. 374 (9701): 1627–1638. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61376-3. PMC 2863325. PMID 19819542. (Erratum: doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61666-8, [1])
- ^ Stephan DA (January 2008). "Unraveling autism". American Journal of Human Genetics. 82 (1): 7–9. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.12.003. PMC 2253980. PMID 18179879.
- ^ Bourgeron, Thomas (September 2015). "From the genetic architecture to synaptic plasticity in autism spectrum disorder". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 16 (9): 551–563. doi:10.1038/nrn3992. PMID 26289574. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ Benger, Matthew; Kinali, Maria; Mazarakis, Nicholas D. (December 2018). "Autism spectrum disorder: prospects for treatment using gene therapy". Molecular Autism. 9 (1): 39. doi:10.1186/s13229-018-0222-8. PMC 6011246. PMID 29951185. Retrieved 26 May 2023.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Sztainberg, Yehezkel; Zoghbi, Huda Y (November 2016). "Lessons learned from studying syndromic autism spectrum disorders". Nature Neuroscience. 19 (11): 1408–1417. doi:10.1038/nn.4420. PMID 27786181. Retrieved 4 June 2023.
- ^ Richards, Caroline; Jones, Christopher; Groves, Laura; Moss, Jo; Oliver, Chris (October 2015). "Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder phenomenology in genetic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Lancet Psychiatry. 2 (10): 909–916. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00376-4. PMID 26341300. Retrieved 27 May 2023.
- ^ a b Fernandez, Bridget A.; Scherer, Stephen W. (31 December 2017). "Syndromic autism spectrum disorders: moving from a clinically defined to a molecularly defined approach". Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience. 19 (4): 353–371. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2017.19.4/sscherer. PMC 5789213. PMID 29398931. Retrieved 4 June 2023.
- ^ Brown EA, Lautz JD, Davis TR, Gniffke EP, VanSchoiack AA, Neier SC, et al. (2018). "Clustering the autisms using glutamate synapse protein interaction networks from cortical and hippocampal tissue of seven mouse models". Molecular Autism. 9 (48): 48. doi:10.1186/s13229-018-0229-1. PMC 6139139. PMID 30237867.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c Abrahams BS, Geschwind DH (May 2008). "Advances in autism genetics: on the threshold of a new neurobiology". Nature Reviews. Genetics. 9 (5): 341–355. doi:10.1038/nrg2346. PMC 2756414. PMID 18414403.
- ^ Buxbaum JD (2009). "Multiple rare variants in the etiology of autism spectrum disorders". Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience. 11 (1): 35–43. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2009.11.1/jdbuxbaum. PMC 3181906. PMID 19432386.
- ^ a b c Rapin I, Tuchman RF (October 2008). "Autism: definition, neurobiology, screening, diagnosis". Pediatric Clinics of North America. 55 (5): 1129–46, viii. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2008.07.005. PMID 18929056.
- ^ Sanders SJ, He X, Willsey AJ, Ercan-Sencicek AG, Samocha KE, Cicek AE, et al. (September 2015). "Insights into Autism Spectrum Disorder Genomic Architecture and Biology from 71 Risk Loci". Neuron. 87 (6): 1215–1233. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.016. PMC 4624267. PMID 26402605.
- ^ Persico AM, Napolioni V (August 2013). "Autism genetics". Behavioural Brain Research. 251: 95–112. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2013.06.012. PMID 23769996. S2CID 15721666.
- ^ Cook EH, Scherer SW (October 2008). "Copy-number variations associated with neuropsychiatric conditions". Nature. 455 (7215): 919–923. Bibcode:2008Natur.455..919C. doi:10.1038/nature07458. PMID 18923514. S2CID 4377899.
- ^ Brandler WM, Antaki D, Gujral M, Noor A, Rosanio G, Chapman TR, et al. (April 2016). "Frequency and Complexity of De Novo Structural Mutation in Autism". American Journal of Human Genetics. 98 (4): 667–679. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.02.018. PMC 4833290. PMID 27018473.
- ^ Beaudet AL (May 2007). "Autism: highly heritable but not inherited". Nature Medicine. 13 (5): 534–536. doi:10.1038/nm0507-534. PMID 17479094. S2CID 11673879.
- ^ a b c Nishiyama M, Oshikawa K, Tsukada Y, Nakagawa T, Iemura S, Natsume T, et al. (February 2009). "CHD8 suppresses p53-mediated apoptosis through histone H1 recruitment during early embryogenesis". Nature Cell Biology. 11 (2): 172–182. doi:10.1038/ncb1831. PMC 3132516. PMID 19151705.
- ^ a b Ronan JL, Wu W, Crabtree GR (May 2013). "From neural development to cognition: unexpected roles for chromatin". Nature Reviews. Genetics. 14 (5): 347–359. doi:10.1038/nrg3413. PMC 4010428. PMID 23568486.
- ^ a b Thompson BA, Tremblay V, Lin G, Bochar DA (June 2008). "CHD8 is an ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling factor that regulates beta-catenin target genes". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 28 (12): 3894–3904. doi:10.1128/mcb.00322-08. PMC 2423111. PMID 18378692.
- ^ Sugathan A, Biagioli M, Golzio C, Erdin S, Blumenthal I, Manavalan P, et al. (October 2014). "CHD8 regulates neurodevelopmental pathways associated with autism spectrum disorder in neural progenitors". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 111 (42): E4468–E4477. Bibcode:2014PNAS..111E4468S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1405266111. PMC 4210312. PMID 25294932.
- ^ Cotney J, Muhle RA, Sanders SJ, Liu L, Willsey AJ, Niu W, et al. (March 2015). "The autism-associated chromatin modifier CHD8 regulates other autism risk genes during human neurodevelopment". Nature Communications. 6 (1): 6404. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.6404C. doi:10.1038/ncomms7404. PMC 4355952. PMID 25752243.
- ^ Wilkinson B, Grepo N, Thompson BL, Kim J, Wang K, Evgrafov OV, et al. (May 2015). "The autism-associated gene chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 8 (CHD8) regulates noncoding RNAs and autism-related genes". Translational Psychiatry. 5 (5): e568. doi:10.1038/tp.2015.62. PMC 4471293. PMID 25989142.
- ^ Cerase A, Young AN, Ruiz NB, Buness A, Sant GM, Arnold M, et al. (April 2021). "Chd8 regulates X chromosome inactivation in mouse through fine-tuning control of Xist expression". Communications Biology. 4 (1): 485. doi:10.1038/s42003-021-01945-1. PMC 8050208. PMID 33859315.
- ^ Crespi BJ (30 June 2016). "Autism As a Disorder of High Intelligence". Frontiers in Neuroscience. 10: 300. doi:10.3389/fnins.2016.00300. PMC 4927579. PMID 27445671.
- ^ Baron-Cohen S (10 November 2020). The pattern seekers: how autism drives human invention. ISBN 978-1-5416-4713-8. OCLC 1204602315.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Chen JA, Peñagarikano O, Belgard TG, Swarup V, Geschwind DH (2015). "The emerging picture of autism spectrum disorder: genetics and pathology". Annu Rev Pathol (Review). 10: 111–44. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-012414-040405. PMID 25621659.
- ^ Werling DM, Brand H, An JY, Stone MR, Zhu L, Glessner JT, et al. (April 2018). "An analytical framework for whole-genome sequence association studies and its implications for autism spectrum disorder". Nature Genetics. 50 (5): 727–736. doi:10.1038/s41588-018-0107-y. PMC 5961723. PMID 29700473.
- ^ Devlin H (14 September 2018). "Thousands of autistic girls and women 'going undiagnosed' due to gender bias". The Guardian.
- ^ Crespi B, Badcock C (June 2008). "Psychosis and autism as diametrical disorders of the social brain" (PDF). The Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 31 (3): 241–61, discussion 261–320. doi:10.1017/S0140525X08004214. PMID 18578904.
- ^ Crespi B, Stead P, Elliot M (January 2010). "Evolution in health and medicine Sackler colloquium: Comparative genomics of autism and schizophrenia". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (Suppl 1): 1736–1741. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.1736C. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906080106. PMC 2868282. PMID 19955444.
- ^ Baron-Cohen S, Knickmeyer RC, Belmonte MK (November 2005). "Sex differences in the brain: implications for explaining autism" (PDF). Science. 310 (5749): 819–823. Bibcode:2005Sci...310..819B. doi:10.1126/science.1115455. PMID 16272115. S2CID 44330420.
- ^ Gardener H, Spiegelman D, Buka SL (August 2011). "Perinatal and neonatal risk factors for autism: a comprehensive meta-analysis". Pediatrics. 128 (2): 344–55. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-1036. PMC 3387855. PMID 21746727.
- ^ a b Gardener H, Spiegelman D, Buka SL (July 2009). "Prenatal risk factors for autism: comprehensive meta-analysis". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 195 (1): 7–14. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.108.051672. PMC 3712619. PMID 19567888.
- ^ a b c Stefanatos GA (December 2008). "Regression in autistic spectrum disorders". Neuropsychology Review. 18 (4): 305–319. doi:10.1007/s11065-008-9073-y. PMID 18956241. S2CID 34658024.
- ^ Vohr BR, Poggi Davis E, Wanke CA, Krebs NF (April 2017). "Neurodevelopment: The Impact of Nutrition and Inflammation During Preconception and Pregnancy in Low-Resource Settings". Pediatrics (Review). 139 (Suppl 1): S38–S49. doi:10.1542/peds.2016-2828F. PMID 28562247. S2CID 28637473.
- ^ Samsam M, Ahangari R, Naser SA (August 2014). "Pathophysiology of autism spectrum disorders: revisiting gastrointestinal involvement and immune imbalance". World Journal of Gastroenterology (Review). 20 (29): 9942–9951. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9942. PMC 4123375. PMID 25110424.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Lyall K, Schmidt RJ, Hertz-Picciotto I (April 2014). "Maternal lifestyle and environmental risk factors for autism spectrum disorders". International Journal of Epidemiology. 43 (2): 443–464. doi:10.1093/ije/dyt282. PMC 3997376. PMID 24518932.
- ^ Lam J, Sutton P, Kalkbrenner A, Windham G, Halladay A, Koustas E, et al. (2016). "A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Multiple Airborne Pollutants and Autism Spectrum Disorder". PLOS ONE. 11 (9): e0161851. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1161851L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161851. PMC 5031428. PMID 27653281.
- ^ a b Newschaffer CJ, Croen LA, Daniels J, Giarelli E, Grether JK, Levy SE, et al. (2007). "The epidemiology of autism spectrum disorders". Annual Review of Public Health. 28: 235–58. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.28.021406.144007. PMID 17367287.
- ^ Kinney DK, Munir KM, Crowley DJ, Miller AM (October 2008). "Prenatal stress and risk for autism". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 32 (8): 1519–1532. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.06.004. PMC 2632594. PMID 18598714.
- ^ Hussain A, Ali S, Ahmed M, Hussain S (July 2018). "The Anti-vaccination Movement: A Regression in Modern Medicine". Cureus. 10 (7): e2919. doi:10.7759/cureus.2919. PMC 6122668. PMID 30186724.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Spencer JP, Trondsen Pawlowski RH, Thomas S (June 2017). "Vaccine Adverse Events: Separating Myth from Reality". American Family Physician. 95 (12): 786–794. PMID 28671426.
- ^ Di Pietrantonj C, Rivetti A, Marchione P, Debalini MG, Demicheli V (November 2021). "Vaccines for measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (11): CD004407. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004407.pub5. PMC 8607336. PMID 34806766.
- ^ a b Gerber JS, Offit PA (February 2009). "Vaccines and autism: a tale of shifting hypotheses". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 48 (4): 456–461. doi:10.1086/596476. PMC 2908388. PMID 19128068.
- ^ Deer B (8 February 2009). "MMR doctor Andrew Wakefield fixed data on autism". The Sunday Times.
- ^ Boseley S (2 February 2010). "Lancet retracts 'utterly false' MMR paper". The Guardian.
- ^ Stratton K, Ford A, Rusch E, Clayton EW, eds. (August 2011). "Influenza Vaccine". Adverse Effects of Vaccines: Evidence and Causality. Committee to Review Adverse Effects of Vaccines, Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice. Washington, D.C.: Institute of Medicine/National Academies Press. doi:10.17226/13164. ISBN 978-0-309-21435-3. PMID 24624471.
- ^ Flaherty DK (October 2011). "The vaccine-autism connection: a public health crisis caused by unethical medical practices and fraudulent science". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 45 (10): 1302–1304. doi:10.1345/aph.1Q318. PMID 21917556. S2CID 39479569.
- ^ Godlee F, Smith J, Marcovitch H (January 2011). "Wakefield's article linking MMR vaccine and autism was fraudulent". BMJ. 342: c7452. doi:10.1136/bmj.c7452. PMID 21209060. S2CID 43640126.
- ^ Tan M, Parkin JE (November 2000). "Route of decomposition of thiomersal (thimerosal)". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 208 (1–2): 23–34. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00514-7. PMID 11064208.
- ^ Waterhouse L (December 2008). "Autism overflows: increasing prevalence and proliferating theories". Neuropsychology Review. 18 (4): 273–286. doi:10.1007/s11065-008-9074-x. PMID 19015994. S2CID 8863638.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions about Thimerosal". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ^ a b Taylor LE, Swerdfeger AL, Eslick GD (June 2014). "Vaccines are not associated with autism: an evidence-based meta-analysis of case-control and cohort studies". Vaccine. 32 (29): 3623–3629. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.04.085. PMID 24814559.
- ^ Vaccines and autism:
- Doja A, Roberts W (November 2006). "Immunizations and autism: a review of the literature". The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. Le Journal Canadien des Sciences Neurologiques. 33 (4): 341–346. doi:10.1017/s031716710000528x. PMID 17168158.
- Gerber JS, Offit PA (February 2009). "Vaccines and autism: a tale of shifting hypotheses". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 48 (4): 456–461. doi:10.1086/596476. PMC 2908388. PMID 19128068.
- Gross L (May 2009). "A broken trust: lessons from the vaccine--autism wars". PLOS Biology. 7 (5): e1000114. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000114. PMC 2682483. PMID 19478850.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Paul R (June 2009). "Parents ask: Am I risking autism if I vaccinate my children?". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 39 (6): 962–963. doi:10.1007/s10803-009-0739-y. PMID 19363650. S2CID 34467853.
- Poland GA, Jacobson RM (January 2011). "The age-old struggle against the antivaccinationists". The New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (2): 97–99. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1010594. PMID 21226573.
- ^ McBrien J, Murphy J, Gill D, Cronin M, O'Donovan C, Cafferkey MT (July 2003). "Measles outbreak in Dublin, 2000". The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 22 (7): 580–584. doi:10.1097/00006454-200307000-00002. PMID 12867830.
- ^ Sarovic D (November 2021). "A Unifying Theory for Autism: The Pathogenetic Triad as a Theoretical Framework". Frontiers in Psychiatry (Review). 12: 767075. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.767075. PMC 8637925. PMID 34867553. S2CID 244119594.
- ^ Markram K, Markram H (21 December 2010). "The intense world theory - a unifying theory of the neurobiology of autism". Frontiers in Human Neuroscience (Review). 4: 224. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2010.00224. PMC 3010743. PMID 21191475.
The proposed neuropathology is hyper-functioning of local neural microcircuits, best characterized by hyper-reactivity and hyper-plasticity. Such hyper-functional microcircuits are speculated to become autonomous and memory trapped leading to the core cognitive consequences of hyper-perception, hyper-attention, hyper-memory and hyper-emotionality. The theory is centered on the neocortex and the amygdala, but could potentially be applied to all brain regions. (...) This may lead to obsessively detailed information processing of fragments of the world and an involuntarily and systematic decoupling of the autist from what becomes a painfully intense world.
- ^ Spikins P (27 March 2017). "How our autistic ancestors played an important role in human evolution". The Conversation.
- ^ Spikins P (6 March 2013). "The Stone Age Origins of Autism". In Fitzgerald M (ed.). Recent Advances in Autism Spectrum Disorders - Volume II.
- ^ Lomelin DE (2010). "An Examination of Autism Spectrum Disorders in Relation to Human Evolution and Life History Theory". Nebraska Anthropologist. 57.
- ^ Reser JE (May 2011). "Conceptualizing the autism spectrum in terms of natural selection and behavioral ecology: the solitary forager hypothesis". Evolutionary Psychology. 9 (2): 207–238. doi:10.1177/147470491100900209. PMID 22947969. S2CID 25378900.
- ^ "Autism may have had advantages in humans' hunter-gatherer past, researcher believes". ScienceDaily. University of Southern California. 3 June 2011.
- ^ Rudacille D (8 July 2011). "Lonely hunters". Spectrum.
- ^ Spikins P, Wright B, Hodgson D (1 October 2016). "Are there alternative adaptive strategies to human pro-sociality? The role of collaborative morality in the emergence of personality variation and autistic traits". Time and Mind. 9 (4): 289–313. doi:10.1080/1751696X.2016.1244949. ISSN 1751-696X. S2CID 151820168.
- ^ Harvard University (11 January 2020). "Ongoing human evolution could explain recent rise in certain disorders". ScienceDaily. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- ^ a b Penn HE (February 2006). "Neurobiological correlates of autism: a review of recent research". Child Neuropsychology. 12 (1): 57–79. doi:10.1080/09297040500253546. PMID 16484102. S2CID 46119993.
- ^ London E (October 2007). "The role of the neurobiologist in redefining the diagnosis of autism". Brain Pathology. 17 (4): 408–411. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00103.x. PMC 8095627. PMID 17919126. S2CID 24860348.
- ^ Israelyan N, Margolis KG (June 2018). "Serotonin as a link between the gut-brain-microbiome axis in autism spectrum disorders". Pharmacological Research (Review). 132: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2018.03.020. PMC 6368356. PMID 29614380.
- ^ a b Wasilewska J, Klukowski M (2015). "Gastrointestinal symptoms and autism spectrum disorder: links and risks - a possible new overlap syndrome". Pediatric Health, Medicine and Therapeutics (Review). 6: 153–166. doi:10.2147/PHMT.S85717. PMC 5683266. PMID 29388597.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Rao M, Gershon MD (September 2016). "The bowel and beyond: the enteric nervous system in neurological disorders". Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology (Review). 13 (9): 517–528. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2016.107. PMC 5005185. PMID 27435372.
immune dysregulation, GI inflammation, malfunction of the ANS, genetic and metabolic activity of the microbiome, and dietary metabolites may contribute to brain dysfunction and neuroinflammation depending upon individual genetic vulnerability
- ^ Betancur C, Sakurai T, Buxbaum JD (July 2009). "The emerging role of synaptic cell-adhesion pathways in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorders" (PDF). Trends in Neurosciences. 32 (7): 402–412. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2009.04.003. PMID 19541375. S2CID 8644511.
- ^ Arndt TL, Stodgell CJ, Rodier PM (2005). "The teratology of autism". International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience. 23 (2–3): 189–199. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2004.11.001. PMID 15749245. S2CID 17797266.
- ^ Koenig K, Tsatsanis KD, Volkmar FR (2001). "Neurobiology and Genetics of Autism: A Developmental Perspective". In Burack JA, Charman T, Yirmiya N, Zelazo PR (eds.). The development of autism: perspectives from theory and research. Mahwah, N.J.: L. Erlbaum. pp. 73–92. ISBN 9780805832457. OCLC 806185029.
- ^ Minshew NJ (April 1996). "Brief report: brain mechanisms in autism: functional and structural abnormalities". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 26 (2): 205–9. doi:10.1007/BF02172013. PMID 8744486. S2CID 8134205.
- ^ Stanfield AC, McIntosh AM, Spencer MD, Philip R, Gaur S, Lawrie SM (June 2008). "Towards a neuroanatomy of autism: a systematic review and meta-analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging studies". European Psychiatry. 23 (4): 289–99. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.05.006. PMID 17765485. S2CID 29070618.
- ^ Lefebvre A, Beggiato A, Bourgeron T, Toro R (July 2015). "Neuroanatomical Diversity of Corpus Callosum and Brain Volume in Autism: Meta-analysis, Analysis of the Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange Project, and Simulation". Biological Psychiatry. 78 (2): 126–34. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.02.010. PMID 25850620. S2CID 8794474.
- ^ Sugranyes G, Kyriakopoulos M, Corrigall R, Taylor E, Frangou S (2011). "Autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia: meta-analysis of the neural correlates of social cognition". PLOS ONE. 6 (10): e25322. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...625322S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025322. PMC 3187762. PMID 21998649.
- ^ a b c d e O'Reilly C, Lewis JD, Elsabbagh M (2017). "Is functional brain connectivity atypical in autism? A systematic review of EEG and MEG studies". PLOS ONE (Review). 12 (5): e0175870. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1275870O. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0175870. PMC 5414938. PMID 28467487.
- ^ Al-Beltagi M (May 2021). "Autism medical comorbidities". World Journal of Clinical Pediatrics. 10 (3): 15–28. doi:10.5409/wjcp.v10.i3.15. PMC 8085719. PMID 33972922.
Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders are significantly more common in children with ASD; they occur in 46% to 84% of them.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h Azhari A, Azizan F, Esposito G (July 2019). "A systematic review of gut-immune-brain mechanisms in Autism Spectrum Disorder". Developmental Psychobiology. 61 (5): 752–771. doi:10.1002/dev.21803. hdl:10220/49107. PMID 30523646. S2CID 54523742.
- ^ Kennedy DP, Adolphs R (November 2012). "The social brain in psychiatric and neurological disorders". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 16 (11): 559–72. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2012.09.006. PMC 3606817. PMID 23047070.
- ^ Schultz RT (2005). "Developmental deficits in social perception in autism: the role of the amygdala and fusiform face area". International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience. 23 (2–3): 125–41. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2004.12.012. PMID 15749240. S2CID 17078137.
- ^ Haas RH, Parikh S, Falk MJ, Saneto RP, Wolf NI, Darin N, Cohen BH (December 2007). "Mitochondrial disease: a practical approach for primary care physicians". Pediatrics. 120 (6): 1326–1333. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-0391. PMID 18055683. S2CID 4939996.
- ^ a b Rossignol DA, Frye RE (March 2012). "Mitochondrial dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Molecular Psychiatry. 17 (3): 290–314. doi:10.1038/mp.2010.136. PMC 3285768. PMID 21263444.
- ^ Gentile S (August 2015). "Prenatal antidepressant exposure and the risk of autism spectrum disorders in children. Are we looking at the fall of Gods?". Journal of Affective Disorders. 182: 132–7. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2015.04.048. PMID 25985383.
- ^ Dragioti E, Solmi M, Favaro A, Fusar-Poli P, Dazzan P, Thompson T, et al. (October 2019). "Association of Antidepressant Use With Adverse Health Outcomes: A Systematic Umbrella Review". JAMA Psychiatry. 76 (12): 1241–1255. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.2859. PMC 6777224. PMID 31577342.
- ^ "Fake and harmful autism 'treatments'". nhs.uk. 2 May 2019. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ "Making information and the words we use accessible". NHS England. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ "How to talk about autism". www.autism.org.uk. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ "The psychiatric management of autism in adults (CR228)". Royal College of Psychiatrists (UK). Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ McPartland J, Klin A (October 2006). "Asperger's syndrome". Adolescent Medicine Clinics. 17 (3): 771–88, abstract xiii. doi:10.1016/j.admecli.2006.06.010 (inactive 31 December 2022). PMID 17030291.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of December 2022 (link) - ^ Woodbury-Smith MR, Volkmar FR (June 2008). "Asperger syndrome". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 18 (1): 2–11. doi:10.1007/s00787-008-0701-0. PMID 18563474. S2CID 12808995.
- ^ Coplan J, Jawad AF (July 2005). "Modeling clinical outcome of children with autistic spectrum disorders". Pediatrics. 116 (1): 117–22. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-1118. PMID 15995041. S2CID 8440775.
- ^ "10 Facts about Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)". Early Childhood Development | ACF. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g Myers SM, Johnson CP (November 2007). "Management of children with autism spectrum disorders". Pediatrics. 120 (5): 1162–1182. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2362. PMID 17967921.
- ^ Ospina MB, Krebs Seida J, Clark B, Karkhaneh M, Hartling L, Tjosvold L, et al. (2008). "Behavioural and developmental interventions for autism spectrum disorder: a clinical systematic review". PLOS ONE. 3 (11): e3755. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.3755O. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003755. PMC 2582449. PMID 19015734.
- ^ a b c d e f Smith T, Iadarola S (2 November 2015). "Evidence Base Update for Autism Spectrum Disorder". Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology. 44 (6). Taylor & Francis: 897–922. doi:10.1080/15374416.2015.1077448. ISSN 1537-4416. PMID 26430947.
- ^ Eldevik S, Hastings RP, Hughes JC, Jahr E, Eikeseth S, Cross S (May 2009). "Meta-analysis of Early Intensive Behavioral Intervention for children with autism". Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology. 38 (3). Taylor & Francis: 439–450. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.607.9620. doi:10.1080/15374410902851739. PMID 19437303. S2CID 205873629.
- ^ a b c d e Smith T, Iadarola S (2015). "Evidence Base Update for Autism Spectrum Disorder". Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology. 44 (6). Taylor & Francis: 897–922. doi:10.1080/15374416.2015.1077448. ISSN 1537-4416. PMID 26430947.
- ^ Matson JL, Dempsey T, Fodstad JC (November 2009). "The effect of Autism Spectrum Disorders on adaptive independent living skills in adults with severe intellectual disability". Research in Developmental Disabilities. 30 (6). Elsevier: 1203–1211. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2009.04.001. eISSN 1873-3379. PMID 19450950.
- ^ "NIMH » Autism Spectrum Disorder". National Institute of Mental Health (US). National Institutes of Health (US). Retrieved 8 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d e Ji N, Findling RL (March 2015). "An update on pharmacotherapy for autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 28 (2): 91–101. doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000132. PMID 25602248. S2CID 206141453.
- ^ a b Wang X, Zhao J, Huang S, Chen S, Zhou T, Li Q, et al. (May 2021). "Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review". Pediatrics. 147 (5). American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). doi:10.1542/peds.2020-049880. PMID 33888566. S2CID 233370479.
- ^ a b Myers SM, Johnson CP (November 2007). "Management of children with autism spectrum disorders". Pediatrics. 120 (5): 1162–1182. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2362. PMID 17967921. S2CID 1656920. Archived from the original on 12 June 2009.
- ^ Sigman M, Capps L (2002). Children with Autism: A Developmental Perspective. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. pp. 178–179. ISBN 978-0-674-05313-7.
- ^ Rogers SJ, Vismara LA (January 2008). "Evidence-based comprehensive treatments for early autism". Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology. 37 (1). Taylor & Francis: 8–38. doi:10.1080/15374410701817808. ISSN 1537-4416. PMC 2943764. PMID 18444052.
- ^ a b Zwaigenbaum L, Bauman ML, Choueiri R, Kasari C, Carter A, Granpeesheh D, et al. (October 2015). "Early Intervention for Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder Under 3 Years of Age: Recommendations for Practice and Research". Pediatrics. 136 (Supplement 1): S60-81. doi:10.1542/peds.2014-3667E. PMC 9923898. PMID 26430170.
- ^ a b c d Reichow B, Hume K, Barton EE, Boyd BA (May 2018). "Early intensive behavioral intervention (EIBI) for young children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD)". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 5 (10): CD009260. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009260.pub3. PMC 6494600. PMID 29742275.
- ^ a b Brignell A, Chenausky KV, Song H, Zhu J, Suo C, Morgan AT (November 2018). "Communication interventions for autism spectrum disorder in minimally verbal children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (11): CD012324. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012324.pub2. PMC 6516977. PMID 30395694.
- ^ a b Weissman L (March 2020). "Autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents: Pharmacologic interventions". Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ^ Williams Buckley A, Hirtz D, Oskoui M, et al. (March 2020). "Practice guideline: Treatment for insomnia and disrupted sleep behavior in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology. 94 (9): 392–404. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000009033. PMC 7238942. PMID 32051244.
- ^ Harrop C (August 2015). "Evidence-based, parent-mediated interventions for young children with autism spectrum disorder: The case of restricted and repetitive behaviors". Autism. 19 (6): 662–72. doi:10.1177/1362361314545685. PMID 25186943. S2CID 32326472.
- ^ Powell K (August 2004). "Opening a window to the autistic brain". PLOS Biology. 2 (8): E267. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020267. PMC 509312. PMID 15314667.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Kanne SM, Randolph JK, Farmer JE (December 2008). "Diagnostic and assessment findings: a bridge to academic planning for children with autism spectrum disorders". Neuropsychology Review. 18 (4): 367–384. doi:10.1007/s11065-008-9072-z. PMID 18855144. S2CID 21108225.
- ^ Simpson RL, de Boer-Ott SR, Smith-Myles B (2003). "Inclusion of Learners with Autism Spectrum Disorders in General Education Settings". Topics in Language Disorders. 23 (2): 116–133. doi:10.1097/00011363-200304000-00005. S2CID 143733343. Archived from the original on 14 July 2011.
- ^ a b Sanchack KE, Thomas CA (December 2016). "Autism Spectrum Disorder: Primary Care Principles". American Family Physician. 94 (12): 972–979. PMID 28075089.
- ^ a b Siafis S, Çıray O, Wu H, Schneider-Thoma J, Bighelli I, Krause M, Rodolico A, Ceraso A, Deste G, Huhn M, Fraguas D, San José Cáceres A, Mavridis D, Charman T, Murphy DG, Parellada M, Arango C, Leucht S (2022). "Pharmacological and dietary-supplement treatments for autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis". Molecular Autism. 13 (1): 10. doi:10.1186/s13229-022-00488-4. PMC 8896153. PMID 35246237.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Oswald DP, Sonenklar NA (June 2007). "Medication use among children with autism spectrum disorders". Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 17 (3): 348–355. doi:10.1089/cap.2006.17303. PMID 17630868.
- ^ Doyle CA, McDougle CJ (September 2012). "Pharmacologic treatments for the behavioral symptoms associated with autism spectrum disorders across the lifespan". Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience. 14 (3): 263–279. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2012.14.3/cdoyle. PMC 3513681. PMID 23226952.
- ^ Leskovec TJ, Rowles BM, Findling RL (2008). "Pharmacological treatment options for autism spectrum disorders in children and adolescents". Harvard Review of Psychiatry. 16 (2): 97–112. doi:10.1080/10673220802075852. PMID 18415882. S2CID 26112061.
- ^ Ameis SH, Kassee C, Corbett-Dick P, Cole L, Dadhwal S, Lai MC, et al. (November 2018). "Systematic review and guide to management of core and psychiatric symptoms in youth with autism". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 138 (5): 379–400. doi:10.1111/acps.12918. PMID 29904907. S2CID 49209337.
- ^ Benevides TW, Shore SM, Andresen ML, Caplan R, Cook B, Gassner DL, et al. (August 2020). "Interventions to address health outcomes among autistic adults: A systematic review". Autism. 24 (6): 1345–1359. doi:10.1177/1362361320913664. PMC 7787674. PMID 32390461.
- ^ a b c Gogou M, Kolios G (June 2018). "Are therapeutic diets an emerging additional choice in autism spectrum disorder management?". World Journal of Pediatrics (Review). 14 (3): 215–223. doi:10.1007/s12519-018-0164-4. PMID 29846886. S2CID 44155118.
Current literature knowledge provides evidence that ketogenic and casein/gluten-free diet may have their own place in our reserve for the therapeutic management of specific subsets of children with autism. ... More clinical studies about the effect of gluten/caseinfree diet in these patients are available. However, available data arise from studies with small sample size and are still controversial. In general, despite encouraging data, no definite proof still exists. Under this view, the use of therapeutic diets in children with autism should be restricted to specific subgroups, such as children with autism and epilepsy or specific inborn errors of metabolism (ketogenic diet), children with known food intolerance/allergy or even children with food intolerance markers (gluten- and casein-free diet). Their implementation should always be guided by health care practitioners.
- ^ Marí-Bauset S, Zazpe I, Mari-Sanchis A, Llopis-González A, Morales-Suárez-Varela M (December 2014). "Evidence of the gluten-free and casein-free diet in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review". Journal of Child Neurology. 29 (12): 1718–1727. doi:10.1177/0883073814531330. hdl:10171/37087. PMID 24789114. S2CID 19874518.
- ^ a b Millward C, Ferriter M, Calver S, Connell-Jones G (April 2008). Ferriter M (ed.). "Gluten- and casein-free diets for autistic spectrum disorder". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD003498. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003498.pub3. PMC 4164915. PMID 18425890.
Knivsberg 2002 "monitoring of the compliance with diet was not carried out" ... "several reports of children 'sneaking food' from siblings or classmates"
- ^ Hyman SL, Stewart PA, Foley J, Cain U, Peck R, Morris DD, et al. (January 2016). "The Gluten-Free/Casein-Free Diet: A Double-Blind Challenge Trial in Children with Autism". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 46 (1): 205–220. doi:10.1007/s10803-015-2564-9. PMID 26343026. S2CID 12884691.
20 natural challenges when parents reported that children by mistake consumed foods containing gluten or casein.
- ^ Siafis S, Çıray O, Schneider-Thoma J, Bighelli I, Krause M, Rodolico A, Ceraso A, Deste G, Huhn M, Fraguas D, Mavridis D, Charman T, Murphy DG, Parellada M, Arango C, Leucht S (2020). "Placebo response in pharmacological and dietary supplement trials of autism spectrum disorder (ASD): systematic review and meta-regression analysis". Molecular Autism. 11 (1): 66. doi:10.1186/s13229-020-00372-z. PMC 7448339. PMID 32847616.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Buie T (May 2013). "The relationship of autism and gluten". Clinical Therapeutics (Review). 35 (5): 578–583. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.04.011. PMID 23688532.
At this time, the studies attempting to treat symptoms of autism with diet have not been sufficient to support the general institution of a gluten-free or other diet for all children with autism. There may be a subgroup of patients who might benefit from a gluten-free diet, but the symptom or testing profile of these candidates remains unclear.
- ^ Volta U, Caio G, De Giorgio R, Henriksen C, Skodje G, Lundin KE (June 2015). "Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: a work-in-progress entity in the spectrum of wheat-related disorders". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Gastroenterology. 29 (3): 477–491. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2015.04.006. PMID 26060112.
autism spectrum disorders (ASD) have been hypothesized to be associated with NCGS [47,48]. Notably, a gluten- and casein-free diet might have a positive effect in improving hyperactivity and mental confusion in some patients with ASD. This very exciting association between NCGS and ASD deserves further study before conclusions can be firmly drawn
- ^ San Mauro Martín I, Garicano Vilar E, Collado Yurrutia L, Ciudad Cabañas MJ (December 2014). "[Is gluten the great etiopathogenic agent of disease in the XXI century?]" [Is gluten the great etiopathogenic agent of disease in the XXI century?]. Nutricion Hospitalaria (in Spanish). 30 (6): 1203–1210. doi:10.3305/nh.2014.30.6.7866. PMID 25433099.
- ^ Tye C, Runicles AK, Whitehouse AJ, Alvares GA (2019). "Characterizing the Interplay Between Autism Spectrum Disorder and Comorbid Medical Conditions: An Integrative Review". Frontiers in Psychiatry (Review). 9: 751. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00751. PMC 6354568. PMID 30733689.
- ^ Levy SE, Hyman SL (October 2008). "Complementary and alternative medicine treatments for children with autism spectrum disorders". Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America (Review). 17 (4): 803–20, ix. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2008.06.004. PMC 2597185. PMID 18775371.
- ^ Brown MJ, Willis T, Omalu B, Leiker R (August 2006). "Deaths resulting from hypocalcemia after administration of edetate disodium: 2003-2005". Pediatrics. 118 (2): e534–e536. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-0858. PMID 16882789. S2CID 28656831. Archived from the original on 27 July 2009.
- ^ James S, Stevenson SW, Silove N, Williams K (May 2015). James S (ed.). "Chelation for autism spectrum disorder (ASD)". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (Review) (5): CD010766. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010766. PMID 26106752.
- ^ Loftus Y (24 November 2021). "CEASE Therapy for Autism: the Controversy of a "Cure"". Autism Parenting Magazine. Autism Parenting Magazine. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Benevides TW, Shore SM, Andresen ML, Caplan R, Cook B, Gassner DL, et al. (August 2020). "Interventions to address health outcomes among autistic adults: A systematic review". Autism. 24 (6): 1345–1359. doi:10.1177/1362361320913664. PMC 7787674. PMID 32390461. S2CID 218586379.
- ^ Geretsegger M, Fusar-Poli L, Elefant C, Mössler KA, Vitale G, Gold C (May 2022). "Music therapy for autistic people". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2022 (5): CD004381. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004381.pub4. PMC 9082683. PMID 35532041.
- ^ Warren Z, Veenstra-VanderWeele J, Stone W, et al. (April 2011). Therapies for Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders (Report No. 11-EHC029-EF). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). p. 8. PMID 21834171.
Hyperbaric therapy, in which oxygen is administered in special chambers that maintain a higher air pressure, has shown possible effects in other chronic neurologic conditions and has also undergone preliminary exploration in ASDs.
[needs update] - ^ Rumayor CB, Thrasher AM (November 2017). "Reflections on Recent Research Into Animal-Assisted Interventions in the Military and Beyond". Current Psychiatry Reports. 19 (12): 110. doi:10.1007/s11920-017-0861-z. PMID 29177710. S2CID 207338873.
- ^ Duchan E, Patel DR (February 2012). "Epidemiology of autism spectrum disorders". Pediatric Clinics of North America. 59 (1): 27–43, ix–x. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2011.10.003. PMID 22284791.
- ^ Lambert N, Strebel P, Orenstein W, Icenogle J, Poland GA (June 2015). "Rubella". Lancet. 385 (9984): 2297–2307. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60539-0. PMC 4514442. PMID 25576992.
- ^ a b Helt M, Kelley E, Kinsbourne M, Pandey J, Boorstein H, Herbert M, Fein D (December 2008). "Can children with autism recover? If so, how?". Neuropsychology Review. 18 (4): 339–366. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.695.2995. doi:10.1007/s11065-008-9075-9. PMID 19009353. S2CID 4317267.
- ^ a b Fein D, Barton M, Eigsti IM, Kelley E, Naigles L, Schultz RT, et al. (February 2013). "Optimal outcome in individuals with a history of autism". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 54 (2): 195–205. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12037. PMC 3547539. PMID 23320807.
- ^ Orinstein AJ, Helt M, Troyb E, Tyson KE, Barton ML, Eigsti IM, et al. (May 2014). "Intervention for optimal outcome in children and adolescents with a history of autism". Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics. 35 (4): 247–256. doi:10.1097/DBP.0000000000000037. PMC 4487510. PMID 24799263.
- ^ Rogers SJ, Vismara LA (January 2008). "Evidence-based comprehensive treatments for early autism". Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology. 37 (1). Taylor & Francis: 8–38. doi:10.1080/15374410701817808. PMC 2943764. PMID 18444052.
- ^ Tidmarsh L, Volkmar FR (September 2003). "Diagnosis and epidemiology of autism spectrum disorders". Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 48 (8): 517–525. doi:10.1177/070674370304800803. PMID 14574827. S2CID 38070709.
- ^ a b Tracy A Becerra-Culqui; Frances L Lynch; Ashli A Owen-Smith; Joseph Spitzer; Lisa A Croen (1 October 2018). "Parental First Concerns and Timing of Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 48 (10): 3367–3376. doi:10.1007/S10803-018-3598-6. ISSN 0162-3257. PMID 29754290. Wikidata Q88651632.
- ^ Dwyer P, Ryan JG, Williams ZJ, Gassner DL (April 2022). "First Do No Harm: Suggestions Regarding Respectful Autism Language". Pediatrics. 149 (Suppl 4). American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). doi:10.1542/peds.2020-049437n. PMC 9066426. PMID 35363298.
- ^ Zwaigenbaum L, Bryson S, Lord C, Rogers S, Carter A, Carver L, et al. (May 2009). "Clinical assessment and management of toddlers with suspected autism spectrum disorder: insights from studies of high-risk infants". Pediatrics. 123 (5): 1383–91. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-1606. PMC 2833286. PMID 19403506.
- ^ Lord C (November 1995). "Follow-up of two-year-olds referred for possible autism". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 36 (8): 1365–82. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1995.tb01669.x. eISSN 1469-7610. ISSN 0021-9630. OCLC 01307942. PMID 8988272.
- ^ Rogers SJ (June 2009). "What are infant siblings teaching us about autism in infancy?". Autism Research. 2 (3): 125–137. doi:10.1002/aur.81. PMC 2791538. PMID 19582867.
- ^ Zwaigenbaum L (October 2001). "Autistic spectrum disorders in preschool children". Canadian Family Physician. 47 (10): 2037–42. PMC 2018435. PMID 11723598.
- ^ a b c Halsey NA, Hyman SL (May 2001). "Measles-mumps-rubella vaccine and autistic spectrum disorder: report from the New Challenges in Childhood Immunizations Conference convened in Oak Brook, Illinois, June 12-13, 2000". Pediatrics. 107 (5): E84. doi:10.1542/peds.107.5.e84. PMID 11331734.
- ^ a b Martínez-Pedraza F, Carter AS (July 2009). "Autism spectrum disorders in young children". Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 18 (3): 645–63. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2009.02.002. PMC 3166636. PMID 19486843.
- ^ a b Werner E, Dawson G, Munson J, Osterling J (June 2005). "Variation in early developmental course in autism and its relation with behavioral outcome at 3-4 years of age". Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 35 (3): 337–50. doi:10.1007/s10803-005-3301-6. PMID 16119475. S2CID 22485657.
- ^ "Autism spectrum disorder – childhood disintegrative disorder: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ^ Annio Posar; Paola Visconti (23 September 2020). "Is it autism? Some suggestions for pediatricians". Türk pediatri arsivi Turkish Pediatrics Archive. 55 (3): 229–235. doi:10.14744/TURKPEDIATRIARS.2020.59862. ISSN 1306-0015. PMC 7536466. PMID 33061749. Wikidata Q100648906.
- ^ a b c d e Ozonoff S, Heung K, Byrd R, Hansen R, Hertz-Picciotto I (December 2008). "The onset of autism: patterns of symptom emergence in the first years of life". Autism Research. 1 (6): 320–328. doi:10.1002/aur.53. PMC 2857525. PMID 19360687.
- ^ a b CDC (18 August 2016). "Part II: A Closer Look". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 15 September 2022.
- ^ Ozonoff S, Iosif AM (May 2019). "Changing conceptualizations of regression: What prospective studies reveal about the onset of autism spectrum disorder". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 100: 296–304. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.03.012. PMC 6451681. PMID 30885812.
- ^ Mash EJ, Barkley RA (2003). Child Psychopathology. New York: The Guilford Press. pp. 409–454. ISBN 9781572306097.
- ^ Ellis Weismer S, Kover ST (December 2015). "Preschool language variation, growth, and predictors in children on the autism spectrum". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 56 (12): 1327–37. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12406. eISSN 1469-7610. ISSN 0021-9630. OCLC 01307942. PMC 4565784. PMID 25753577.
- ^ Dawson G, Osterling J (1997). "Early Intervention in Autism". In Guralnick MJ (ed.). The effectiveness of early intervention. Baltimore: Brookes. pp. 307–326. ISBN 1-55766-255-X. OCLC 34411043. ERIC ED414694.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Stichter JP, Riley-Tillman TC, Jimerson SR (December 2016). "Assessing, understanding, and supporting students with autism at school: Contemporary science, practice, and policy". School Psychology Quarterly. 31 (4): 443–449. doi:10.1037/spq0000184. PMID 27929316.
- ^ a b c d Hahler EM, Elsabbagh M (1 March 2015). "Autism: A Global Perspective". Current Developmental Disorders Reports. 2 (1): 58–64. doi:10.1007/s40474-014-0033-3. ISSN 2196-2987. S2CID 73214418.
- ^ McLeod S (6 April 2022). "Jean Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development". Simply Psychology. Archived from the original on 1 June 2022. Retrieved 19 February 2019.
- ^ "Facts and Statistics". Autism Society. Archived from the original on 30 October 2019. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
- ^ Hendricks DR, Wehman P (24 March 2009). "Transition From School to Adulthood for Youth With Autism Spectrum Disorders: Review and Recommendations". Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities. 24 (2): 77–88. doi:10.1177/1088357608329827. S2CID 14636906.
- ^ Roux AM, Rast JE, Rava JA, Anderson KA, Shattuck PT (31 August 2015). "Employment Outcomes of Young Adults on the Autism Spectrum". Life Course Outcomes Research Program, A.J. Drexel Autism Institute. Philadelphia, PA: Drexel University.
- ^ Steinhausen HC, Mohr Jensen C, Lauritsen MB (June 2016). "A systematic review and meta-analysis of the long-term overall outcome of autism spectrum disorders in adolescence and adulthood". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 133 (6): 445–452. doi:10.1111/acps.12559. PMID 26763353. S2CID 12341774.
- ^ a b Ohl A, Grice Sheff M, Small S, Nguyen J, Paskor K, Zanjirian A (2017). "Predictors of employment status among adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder". Work. 56 (2): 345–355. doi:10.3233/WOR-172492. PMID 28211841.
- ^ Ganz ML (April 2007). "The lifetime distribution of the incremental societal costs of autism". Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine. 161 (4): 343–349. doi:10.1001/archpedi.161.4.343. PMID 17404130.
- ^ Praslova, Ludmila N. (13 December 2021). "Autism Doesn't Hold People Back at Work. Discrimination Does". Harvard Business Review. ISSN 0017-8012. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- ^ Praslova, Ludmila N. (1 April 2022). "Your "Autism Awareness Day" Might Be Excluding Autistic People". Harvard Business Review. ISSN 0017-8012. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- ^ Johnson KR, Ennis-Cole D, Bohamgregory M (21 February 2020). "Workplace Success Strategies for Employees With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A New Frontier for Human Resource Development". Human Resource Development Review. 19 (2): 122–151. doi:10.1177/1534484320905910. S2CID 213995367.
- ^ Bernick M (12 January 2021). "The State Of Autism Employment In 2021". Forbes. Retrieved 11 February 2022.
- ^ Praslova, Ludmila N. (21 June 2022). "An Intersectional Approach to Inclusion at Work". Harvard Business Review. ISSN 0017-8012. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- ^ Praslova, Ludmila N. (2022). To build a healthy workplace, you need a toxic culture alarm Fast Company, 14 March 2022.
- ^ "Autism". World Health Organization. 30 March 2022. Retrieved 8 May 2022.
- ^ a b c Russell G, Stapley S, Newlove-Delgado T, Salmon A, White R, Warren F, et al. (August 2021). "Time trends in autism diagnosis over 20 years: a UK population-based cohort study". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 63 (6): 674–682. doi:10.1111/jcpp.13505. eISSN 1469-7610. ISSN 0021-9630. OCLC 01307942. PMID 34414570. S2CID 237242123.
The figure starkly illustrates an overall 787% increase in recorded incidence of autism diagnosis over 20 years.
- ^ Maenner MJ, Shaw KA, Baio J, Washington A, Patrick M, DiRienzo M, et al. (March 2020). "Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years - Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2016". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance Summaries. 69 (4): 1–12. doi:10.15585/mmwr.ss6904a1. PMC 7119644. PMID 32214087.
- ^ ICD-11, "Females diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder are more frequently diagnosed with co-occurring disorders of intellectual development, suggesting that less severe presentations may go undetected as compared to males".
- ^ Tsakanikos E, Underwood L, Kravariti E, Bouras N, McCarthy J (2011). "Gender differences in co-morbid psychopathology and clinical management in adults with autism spectrum disorders". Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders. 5 (2): 803–808. doi:10.1016/j.rasd.2010.09.009. ISSN 1750-9467.
- ^ Hollander E, Hagerman RJ, Fein D (30 April 2018). Autism spectrum disorders (First ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association Publishing. ISBN 978-1-61537-192-1. OCLC 1022084798.
- ^ Baio J, Wiggins L, Christensen DL, et al. (April 2018). "Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years – Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2014". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance Summaries. 67 (6): 1–23. doi:10.15585/mmwr.ss6706a1. PMC 5919599. PMID 29701730.
- ^ Rødgaard EM, Jensen K, Vergnes JN, Soulières I, Mottron L (August 2019). "Temporal Changes in Effect Sizes of Studies Comparing Individuals With and Without Autism: A Meta-analysis". JAMA Psychiatry. 76 (11): 1124–1132. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.1956. PMC 6704749. PMID 31433441.
- ^ "CDC estimates 1 in 68 school-aged children have autism; no change from previous estimate". CDC Newsroom. CDC. 31 March 2016. Retrieved 31 December 2019.
- ^ Hill AP (2014). "Epidemiology of autism spectrum disorders". In Volkmar FR (ed.). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders. Diagnosis, Development, and Brain Mechanisms. Vol. 1. New York: Wiley. pp. 57–96. doi:10.1002/9781118911389. ISBN 9781118911389.
- ^ Brugha T, Cooper SA, McManus S, Purdon S, Smith J, Scott FJ, et al. (31 January 2012). "Estimating the prevalence of autism spectrum conditions in adults: extending the 2007 Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey" (PDF). The Information Centre for Health and Social Care. National Health Service, UK. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 December 2014. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ Mozes A (26 November 2018). "Report: Autism Rate Rises to 1 in 40 Children". WebMD. Retrieved 26 September 2019.
- ^ "Autism". www.who.int. Retrieved 15 September 2022.
- ^ a b Fombonne E (June 2009). "Epidemiology of pervasive developmental disorders". Pediatric Research. 65 (6): 591–598. doi:10.1203/PDR.0b013e31819e7203. PMID 19218885.
- ^ Wing L, Potter D (2002). "The epidemiology of autistic spectrum disorders: is the prevalence rising?". Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews. 8 (3): 151–161. doi:10.1002/mrdd.10029. PMID 12216059.
- ^ Gernsbacher MA, Dawson M, Goldsmith HH (April 2005). "Three Reasons Not to Believe in an Autism Epidemic". Current Directions in Psychological Science. 14 (2): 55–58. doi:10.1111/j.0963-7214.2005.00334.x. PMC 4232964. PMID 25404790.
- ^ Rutter M (January 2005). "Incidence of autism spectrum disorders: changes over time and their meaning". Acta Paediatrica. 94 (1): 2–15. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.2005.tb01779.x. PMID 15858952. S2CID 79259285.
- ^ Szpir M (July 2006). "Tracing the origins of autism: a spectrum of new studies". Environmental Health Perspectives. 114 (7): A412–A418. doi:10.1289/ehp.114-a412. PMC 1513312. PMID 16835042.
- ^ Chaste P, Leboyer M (September 2012). "Autism risk factors: genes, environment, and gene-environment interactions". Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience. 14 (3): 281–292. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2012.14.3/pchaste. PMC 3513682. PMID 23226953.
- ^ Schaafsma SM, Pfaff DW (August 2014). "Etiologies underlying sex differences in Autism Spectrum Disorders". Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology. 35 (3): 255–71. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.03.006. PMID 24705124. S2CID 7636860.
- ^ Bertoglio K, Hendren RL (March 2009). "New developments in autism". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 32 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2008.10.004. PMID 19248913.
- ^ Maenner, Matthew J.; Warren, Zachary; Williams, Ashley Robinson; et al. (2023). "Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 sites, United States, 2020". MMWR Surveillance Summaries. 72 (2): 1–14. doi:10.15585/mmwr.ss7202a1. ISSN 1546-0738. PMC 8639024. PMID 34855725. S2CID 257735672.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Shapiro J (26 June 2006). "Autism Movement Seeks Acceptance, Not Cures". NPR. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- ^ Trivedi B. "Autistic and proud of it". New Scientist. Reed Elsevier. ISSN 0262-4079. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- ^ a b c Solomon A (25 May 2008). "The autism rights movement". New York. ISSN 0028-7369. Archived from the original on 27 May 2008. Retrieved 27 May 2008.
- ^ The Economic World. New York city: Chronicle Publishing Company. 1917. p. 366.
- ^ Silverman C (2008). "Fieldwork on another planet: social science perspectives on the autism spectrum". BioSocieties. 3 (3): 325–341. doi:10.1017/S1745855208006236. S2CID 145379758.
- ^ "Results and Analysis of the Autistic Not Weird 2022 Autism Survey - Autistic Not Weird". 23 March 2022. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ "World Autism Awareness Day, 2 April". United Nations. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ^ Bascom J (18 June 2015). "Autistic Pride Day 2015: A Message to the Autistic Community". Retrieved 18 November 2015.
- ^ "Autism Sunday – Home". Autism Sunday. 2010. Archived from the original on 3 March 2010. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ^ "About Autreat". Autreat.com. 2013. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ^ Silverman C (2008). "Fieldwork on Another Planet: Social Science Perspectives on the Autism Spectrum". BioSocieties. 3 (3): 325–341. doi:10.1017/S1745855208006236. ISSN 1745-8552. S2CID 145379758.
- ^ Russell G, Kapp SK, Elliott D, Elphick C, Gwernan-Jones R, Owens C (13 April 2019). "Mapping the Autistic Advantage from the Accounts of Adults Diagnosed with Autism: A Qualitative Study". Autism in Adulthood. 1 (2): 124–133. doi:10.1089/aut.2018.0035. PMC 6493410. PMID 31058260. S2CID 142504027.
- ^ Pellicano E, den Houting J (April 2022). "Annual Research Review: Shifting from 'normal science' to neurodiversity in autism science". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 63 (4): 381–396. doi:10.1111/jcpp.13534. PMC 9298391. PMID 34730840. S2CID 241118562.
- ^ Clarke J, van Amerom G (2007). "'Surplus suffering': differences between organizational understandings of Asperger's syndrome and those people who claim the 'disorder'". Disability & Society. 22 (7): 761–76. doi:10.1080/09687590701659618. S2CID 145736625.
- ^ Baron-Cohen S (2002). "Is Asperger syndrome necessarily viewed as a disability?". Focus Autism Other Dev Disabl. 17 (3): 186–91. doi:10.1177/10883576020170030801. S2CID 145629311. A preliminary, freely readable draft, with slightly different wording in the quoted text, is in: Baron-Cohen S (2002). "Is Asperger's syndrome necessarily a disability?" (PDF). Cambridge: Autism Research Centre. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2008. Retrieved 2 December 2008.
- ^ "The Autism Rights Movement". nymag.com. 23 May 2008. Retrieved 26 October 2021.
- ^ Morgan J (1 October 2016). "Autism spectrum disorder: difference or disability?". The Lancet Neurology. 15 (11): 1126. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30002-3. ISSN 1474-4422. S2CID 54341655.
- ^ Silverman C (1 September 2008). "Fieldwork on Another Planet: Social Science Perspectives on the Autism Spectrum". BioSocieties. 3 (3): 325–341. doi:10.1017/S1745855208006236. ISSN 1745-8560. S2CID 145379758.
- ^ "A medical condition or just a difference? The question roils autism community". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 15 October 2021.
- ^ a b Ratner P (10 July 2016). "Should Autism Be Cured or Is "Curing" Offensive?". Big Think. Retrieved 16 June 2019.
- ^ a b Jaarsma P, Welin S (March 2012). "Autism as a natural human variation: reflections on the claims of the neurodiversity movement". Health Care Analysis. 20 (1): 20–30. doi:10.1007/s10728-011-0169-9. PMID 21311979. S2CID 18618887.
- ^ McGee M (August 2012). "Neurodiversity". Contexts. 11 (3): 12–13. doi:10.1177/1536504212456175. S2CID 220720495.
- ^ Sarrett J (April 2016). "Biocertification and Neurodiversity the Role and Implications of Self-Diagnosis in Autistic Communities". www.researchgate.net. Retrieved 6 March 2022.
- ^ Morgan, Jules (1 October 2016). "Autism spectrum disorder: difference or disability?". The Lancet Neurology. 15 (11): 1126. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30002-3. ISSN 1474-4422. S2CID 54341655.
- ^ Silverman, Chloe (1 September 2008). "Fieldwork on Another Planet: Social Science Perspectives on the Autism Spectrum". BioSocieties. 3 (3): 325–341. doi:10.1017/S1745855208006236. ISSN 1745-8560. S2CID 145379758.
- ^ a b Solomon, Debra (2018). The History of the Autism Puzzle Piece Ribbon. Spectrum Strategies.
- ^ a b Morgan, Julian (2018). Going Gold For Autism Acceptance. Autistic UK.
- ^ Muzikar, Debra (2019). "The Autism Puzzle Piece: A symbol that's going to stay or go?". The Art of Autism.
- ^ Willingham, Emily (2017). "No Foolin': Forget About Autism Awareness And Lighting Up Blue". Forbes.
- ^ Franco, Janelle (2014). "Puzzle Piece Project and Autism Awareness Month." Autism Speaks.
- ^ There have been multiple conversations about the flag on Reddit. Take for example: Reddit (2019). "I tried creating an autism/neurodiversity flag. It's a work in progress."; Reddit (2022). "Autism pride flag goes hard." and Reddit (2022). "where did this flag even come from? first time i ever saw it was during r/place, now i see it everywhere."
- ^ AU-TI (2021). "A New Autistic Pride Flag Has Suddenly Appeared & It's Amazing". AU-TI.
- ^ Shanafelt, Robert (2016). "The nature of flag power: How flags entail dominance, subordination, and social solidarity." Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Du, Xuehong; Jiao, Jianxin; Tseng, Mitchell M. (2003). "Identifying customer need patterns for customization and personalization". Integrated Manufacturing Systems. 14 (5): 387–396. doi:10.1108/09576060310477799.
- ^ Kalyanaraman, Sriram & Sundar, S. Shyam (2006). "The Psychological Appeal of Personalized Content in Web Portals: Does Customization Affect Attitudes and Behavior?" Journal of Communication, Vol. 56, p. 110–132
- ^ Aguiar MC, de Pondé MP (March 2019). "Parenting a child with autism". Jornal Brasileiro de Psiquiatria. 68 (1): 42–47. doi:10.1590/0047-2085000000223. ISSN 0047-2085. S2CID 165119472. Retrieved 17 February 2021.
- ^ Levinovitz A (29 April 2015). "An Alternative-Medicine Believer's Journey Back to Science". WIRED. Retrieved 13 February 2017.
The entire diagnosis and explanation took no more than 45 minutes. 'In the moment of diagnosis, it feels like the death of your hopes and dreams,' Louise [Laidler] says. There's a quiet grief in her voice, even though two decades have passed. 'In a way, it's even harder than a death, because you can't mourn and go on,' she says. 'You have to figure out how to care for your new child.'
- ^ Karst JS, Van Hecke AV (September 2012). "Parent and family impact of autism spectrum disorders: a review and proposed model for intervention evaluation". Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review. 15 (3): 247–77. doi:10.1007/s10567-012-0119-6. PMID 22869324. S2CID 19170894.
- ^ Montes G, Halterman JS (April 2008). "Association of childhood autism spectrum disorders and loss of family income". Pediatrics. 121 (4): e821–e826. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-1594. PMID 18381511. S2CID 55179. Archived from the original on 4 March 2010.
- ^ Montes G, Halterman JS (July 2008). "Child care problems and employment among families with preschool-aged children with autism in the United States". Pediatrics. 122 (1): e202–e208. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-3037. PMID 18595965. S2CID 22686553. Archived from the original on 6 December 2009.
- ^ Orsmond GI, Seltzer MM (2007). "Siblings of individuals with autism spectrum disorders across the life course" (PDF). Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews. 13 (4): 313–320. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.359.7273. doi:10.1002/mrdd.20171. PMID 17979200. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 May 2013.
Sources
- "Neurodevelopmental Disorders". Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. 18 March 2022. ISBN 9780890425770. LCCN 2021051782.
- "6A02 Autism spectrum disorder". International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision (ICD-11). World Health Organisation. February 2022 [adopted in 2019]. 6A02. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
Further reading
- Gabovitch, Elaine; Dutra, Courtney; Lauer, Emily. (2016). The Healthy People 2020 Roadmap for Massachusetts Children & Youth with ASD/DD: Understanding Needs and Measuring Outcomes (Report). Worcester: UMASS Chan Medical School. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
- Matson JL, Dempsey T (2008). "Stereotypy in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Relationship and Diagnostic Fidelity". Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 20(2) 155–165. doi 10.1007/s10882-007-9086-0. S2CID 143874013.
- Johnny L Matson; Michael L Matson; Tessa T Rivet (September 2007). "Social-skills treatments for children with autism spectrum disorders: an overview". Behavior Modification. 31 (5): 682–707. doi:10.1177/0145445507301650. ISSN 0145-4455. PMID 17699124. Wikidata Q28240738.
- Johnny L Matson; Mary Shoemaker (14 July 2009). "Intellectual disability and its relationship to autism spectrum disorders". Research in Developmental Disabilities. 30 (6): 1107–1114. doi:10.1016/J.RIDD.2009.06.003. ISSN 0891-4222. PMID 19604668. Wikidata Q37552242. eISSN 1873-3379
- Pedersen AL, Pettygrove S, Lu Z, Andrews J, Meaney FJ, Kurzius-Spencer M, et al. (August 2017). "DSM Criteria that Best Differentiate Intellectual Disability from Autism Spectrum Disorder". Child Psychiatry and Human Development. 48 (4): 537–545. doi:10.1007/s10578-016-0681-0. PMID 27558812. S2CID 4377173.
- Volkmar FR, Wiesner LA (2009). A practical guide to autism: what every parent, family member, and teacher needs to know. Hoboken: Wiley. ISBN 9780470394731. OCLC 748908084. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
