Portal:Liberia
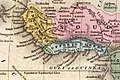
The Liberia Portal 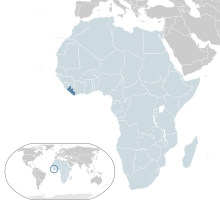 Liberia (/laɪˈbɪəriə/ ), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean to its south and southwest. It has a population of around five and one-half million and covers an area of 43,000 square miles (111,369 km2). The country's official language is English; however, over 20 indigenous languages are spoken, reflecting the country's ethnic and cultural diversity. The capital and largest city is Monrovia. Liberia began in the early 19th century as a project of the American Colonization Society (ACS), which believed black people would face better chances for freedom and prosperity in Africa than in the United States. Between 1822 and the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, more than 15,000 freed and free-born African Americans, along with 3,198 Afro-Caribbeans, relocated to Liberia. Gradually developing an Americo-Liberian identity, the settlers carried their culture and tradition with them. Liberia declared independence on July 26, 1847, which the U.S. did not recognize until February 5, 1862. Liberia was the first African republic to proclaim its independence and is Africa's first and oldest modern republic. Along with Ethiopia, it was one of the two African countries to maintain its sovereignty and independence during the European colonial "Scramble for Africa". During World War II, Liberia supported the United States war effort against Germany, and in turn received considerable American investment in infrastructure, which aided the country's wealth and development. President William Tubman encouraged economic and political changes that heightened the country's prosperity and international profile; Liberia was a founding member of the League of Nations, United Nations, and the Organisation of African Unity. The Americo-Liberian settlers did not relate well to the indigenous peoples they encountered. Colonial settlements were raided by the Kru and Grebo from their inland chiefdoms. Americo-Liberians formed into a small elite that held disproportionate political power; indigenous Africans were excluded from birthright citizenship in their own land until 1904. In 1980, political tensions from the rule of William R. Tolbert resulted in a military coup, marking the end of Americo-Liberian rule and the seizure of power of Liberia's first indigenous leader, Samuel Doe. Establishing a dictatorial regime, Doe was assassinated in 1990 in the context of the First Liberian Civil War which ran from 1989 until 1997 with the election of rebel leader Charles Taylor as president. In 1998, the Second Liberian Civil War erupted against his own dictatorship, and Taylor was overthrown by the end of the war in 2003. The two wars resulted in the deaths of 250,000 people (about 8% of the population) and the displacement of many more, with Liberia's economy shrinking by 90%. A peace agreement in 2003 led to democratic elections in 2005. The country has remained relatively stable since then. (Full article...) Selected article -Fatima Massaquoi-Fahnbulleh (/ˈmæsækwɑː/; 25 December 1911 – 26 November 1978) was a Liberian writer and academic. After completing her education in the United States, she returned to Liberia in 1946, making significant contributions to the cultural and social life of the country. Born into a family of African royalty, Massaquoi grew up in the care of an aunt in Njagbacca, in the Garwula District of Grand Cape Mount County of southern Liberia. After seven years, she returned to the northwestern part of the country in Montserrado County, where she began her schooling. In 1922 she accompanied her father, a diplomat, to Hamburg, Germany, where she completed her school education and started a course in biology at the University of Hamburg. In 1937 she moved to the United States for further education, studying sociology and anthropology at Lane College, Fisk University and Boston University. While in the US, she collaborated on a dictionary of the Vai language and wrote her autobiography, though a legal battle ensued over the rights to her story. She won an injunction barring others from publishing it, and returned to Liberia in 1946, immediately beginning collaboration to establish a university there, which would become the University of Liberia. Committed to national cultural preservation and expansion, Massaquoi served as the director, later dean, of the Liberal Arts College and was the founding director of the Institute of African Studies. She co-founded the Society of Liberian Authors, helped abolish the practice of usurping African names for Westernized versions, and worked towards standardization of the Vai script. In the late 1960s, Vivian Seton, Massaquoi's daughter, had the autobiographical manuscript microfilmed for preservation. After Massaquoi's death, her writings and notes were rediscovered, edited and published in 2013 as The Autobiography of an African Princess. (Full article...)Did you know -
More Did you know (auto generated)
Selected image -TopicsCities and townsRelated portalsWikiProjectsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
SourcesDiscover Wikipedia using portals |